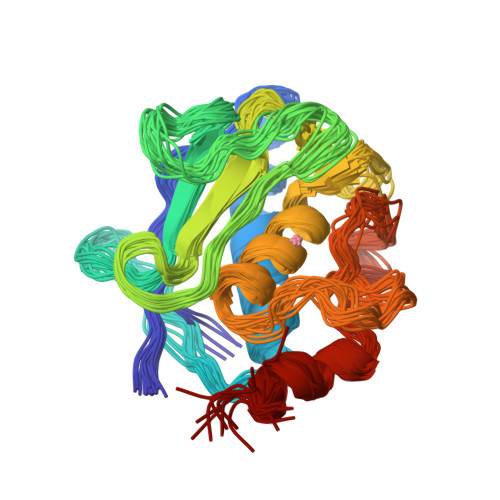
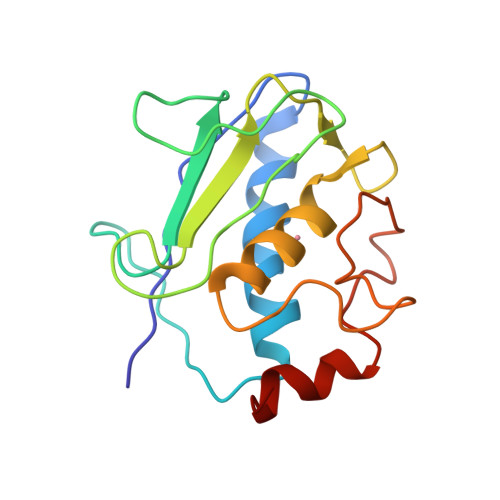
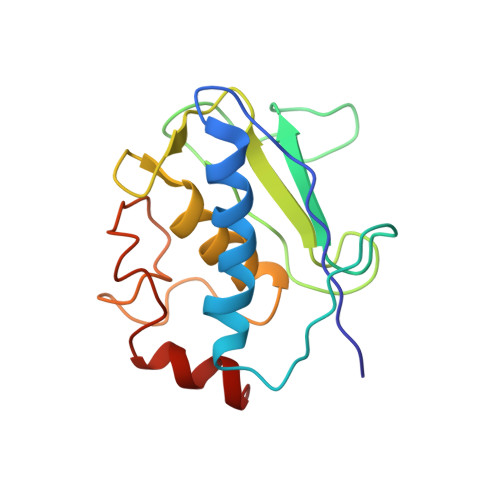
High-resolution solid-state NMR structure of a 17.6 kDa protein.
Bertini, I., Bhaumik, A., De Paepe, G., Griffin, R.G., Lelli, M., Lewandowski, J.R., Luchinat, C.(2010) J Am Chem Soc 132: 1032-1040
- PubMed: 20041641
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/ja906426p
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KRJ - PubMed Abstract:
The use of pseudocontact shifts arising from paramagnetic metal ions in a microcrystalline protein sample is proposed as a strategy to obtain unambiguous signal assignments in solid-state NMR spectra enabling distance extraction for protein structure calculation. With this strategy, 777 unambiguous (281 sequential, 217 medium-range, and 279 long-range) distance restraints could be obtained from PDSD, DARR, CHHC, and the recently introduced PAR and PAIN-CP solid-state experiments for the cobalt(II)-substituted catalytic domain of matrix metalloproteinase 12 (159 amino acids, 17.6 kDa). The obtained structure is a high resolution one, with backbone rmsd of 1.0 +/- 0.2 A, and is in good agreement with the X-ray structure (rmsd to X-ray 1.3 A). The proposed strategy, which may be generalized for nonmetalloproteins with the use of paramagnetic tags, represents a significant step ahead in protein structure determination using solid-state NMR.
Organizational Affiliation:
Magnetic Resonance Center, CERM, University of Florence, Via L. Sacconi, 6-50019 Sesto Fiorentino, Italy. bertini@cerm.unifi.it