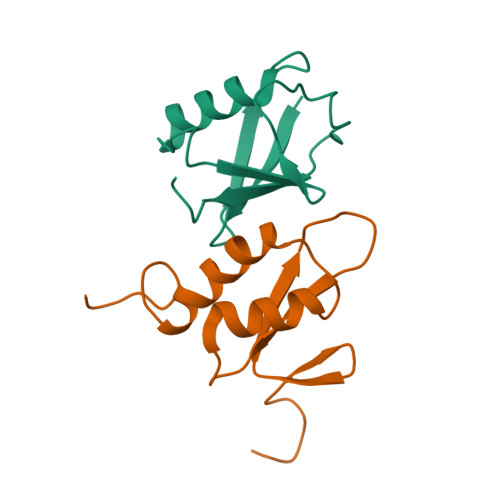
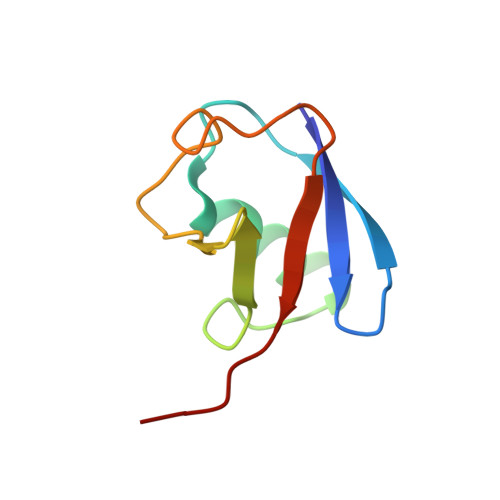
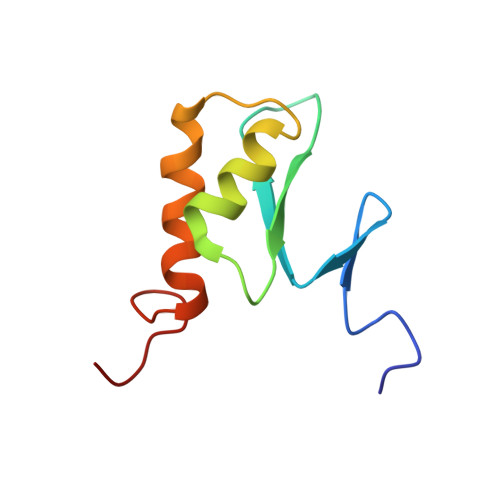
Structural Basis for Ubiquitin Recognition by a Novel Domain from Human Phospholipase A2-activating Protein.
Fu, Q.S., Zhou, C.J., Gao, H.C., Jiang, Y.J., Zhou, Z.R., Hong, J., Yao, W.M., Song, A.X., Lin, D.H., Hu, H.Y.(2009) J Biological Chem 284: 19043-19052
- PubMed: 19423704
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.009126
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2K89, 2K8A, 2K8B, 2K8C - PubMed Abstract:
Ubiquitin (Ub) is an essential modifier conserved in all eukaryotes from yeast to human. Phospholipase A(2)-activating protein (PLAA), a mammalian homolog of yeast DOA1/UFD3, has been proposed to be able to bind with Ub, which plays important roles in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation, vesicle formation, and DNA damage response. We have identified a core domain from the PLAA family ubiquitin-binding region of human PLAA (residues 386-465, namely PFUC) that can bind Ub and elucidated its solution structure and Ub-binding mode by NMR approaches. The PFUC domain possesses equal population of two conformers in solution by cis/trans-isomerization, whereas the two isomers exhibit almost equivalent Ub binding abilities. This domain structure takes a novel fold consisting of four beta-strands and two alpha-helices, and the Ub-binding site on PFUC locates in the surface of alpha2-helix, which is to some extent analogous to those of UBA, CUE, and UIM domains. This study provides structural basis and biochemical information for Ub recognition of the novel PFU domain from a PLAA family protein that may connect ubiquitination and degradation in endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Shanghai Institutes for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 200031, China.