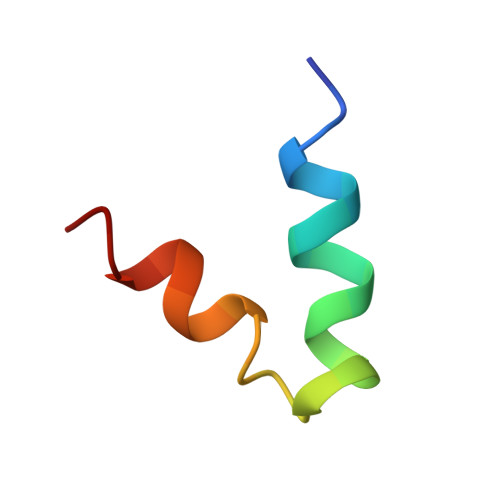
Solution structure of the HsapBK K+-channel voltage-sensor paddle sequence
Unnerstale, S., Lind, J., Papadopoulos, E., Maler, L.(2009) Biochemistry
- PubMed: 19456106
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi9004599
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2K44 - PubMed Abstract:
Voltage-gated potassium channels open and close in response to changes in the membrane potential. In this study, we have determined the NMR solution structure of the putative S3b-S4 voltage-sensor paddle fragment, the part that moves to mediate voltage gating, of the HsapBK potassium channel in dodecylphosphocholine (DPC) micelles. This paper presents the first structure of the S3b-S4 fragment from a BK channel. Diffusion coefficients as determined from PFG NMR experiments showed that a well-defined complex between the peptide and DPC molecules was formed. The structure reveals a helix-turn-helix motif, which is in agreement with crystal structures of other voltage-gated potassium channels, thus indicating that it is feasible to study the isolated fragment. The paddle motifs generally contain several basic residues, implicated in the gating. The critical Arg residues in this structure all reside on the surface, which is in agreement with crystal structures of K(v) channels. Similarities in the structure of the S3b-S4 fragment in BK and K(v) channels as well as important differences are seen, which may be important for explaining the details in paddle movement within a bilayer.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Center for Biomembrane Research, The Arrhenius Laboratories for Natural Sciences, Stockholm University, SE-106 91 Stockholm, Sweden.