Investigating the Substrate Specificity and Oligomerisation of the Leader Protease of Foot and Mouth Disease Virus using NMR
Cencic, R., Mayer, C., Juliano, M.A., Juliano, L., Konrat, R., Kontaxis, G., Skern, T.(2007) J Mol Biology 373: 1071-1087
- PubMed: 17897674
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.08.061
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JQF, 2JQG - PubMed Abstract:
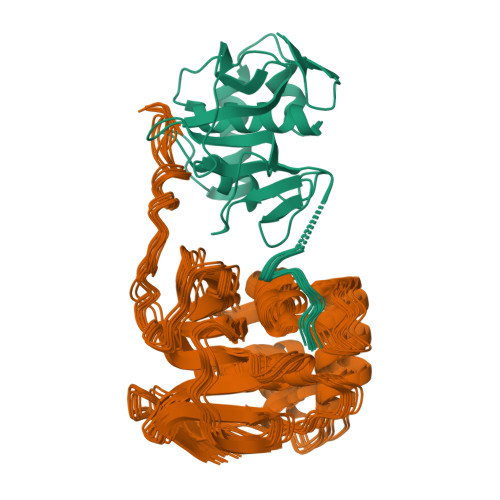
The leader protease (Lbpro) of foot-and-mouth disease virus frees itself during translation from the viral polyprotein by cleavage between its own C terminus and the N terminus of the subsequent protein, VP4. Lbpro also specifically cleaves the host proteins eukaryotic initiation factor (eIF) 4GI and 4GII, thus disabling host cell protein synthesis. We used NMR to study full-length Lbpro as well as a shortened species lacking six C-terminal amino acid residues (sLbpro) to examine the mechanism of self-processing, the quaternary structure and the substrate specificity. Both Lbpro forms have the same structure in solution as in the crystal. In the solution structure of sLbpro, the 12 residue C-terminal extension was flexible and disordered. In contrast, the 18 residue C-terminal extension of full-length Lbpro was bound by the substrate-binding site of a neighbouring molecule, resulting in the formation of a stable dimer in solution. The Lbpro dimer could not be dissociated by increasing the ionic strength or by dilution. Furthermore, titration with model peptides mimicking the substrates destabilised the dimer interface without dissociating the dimer. The peptides were, however, bound by sLbpro in the canonical substrate binding site. Peptide binding gave rise to chemical shifts of residues around the sLbpro substrate binding site. Shifts of Asn146 and Glu147 indicated that these residues might form the enzyme's S1' site and interact with the P1' arginine residue of the eIF4GI cleavage site. Furthermore, differences in substrate specificity between sLbpro and Lbpro observed with an in vitro translated protein indicate some involvement of the C terminus in substrate recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max F. Perutz Laboratories, Medical University of Vienna, Dr. Bohr-Gasse 9/3, A-1030 Vienna, Austria.