Lumazine Synthase from Candida Albicans as an Anti- Fungal Target Enzyme: Structural and Biochemical Basis for Drug Design.
Morgunova, E., Saller, S., Haase, I., Cushman, M., Bacher, A., Fischer, M., Ladenstein, R.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 17231
- PubMed: 17446177
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M701724200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2JFB - PubMed Abstract:
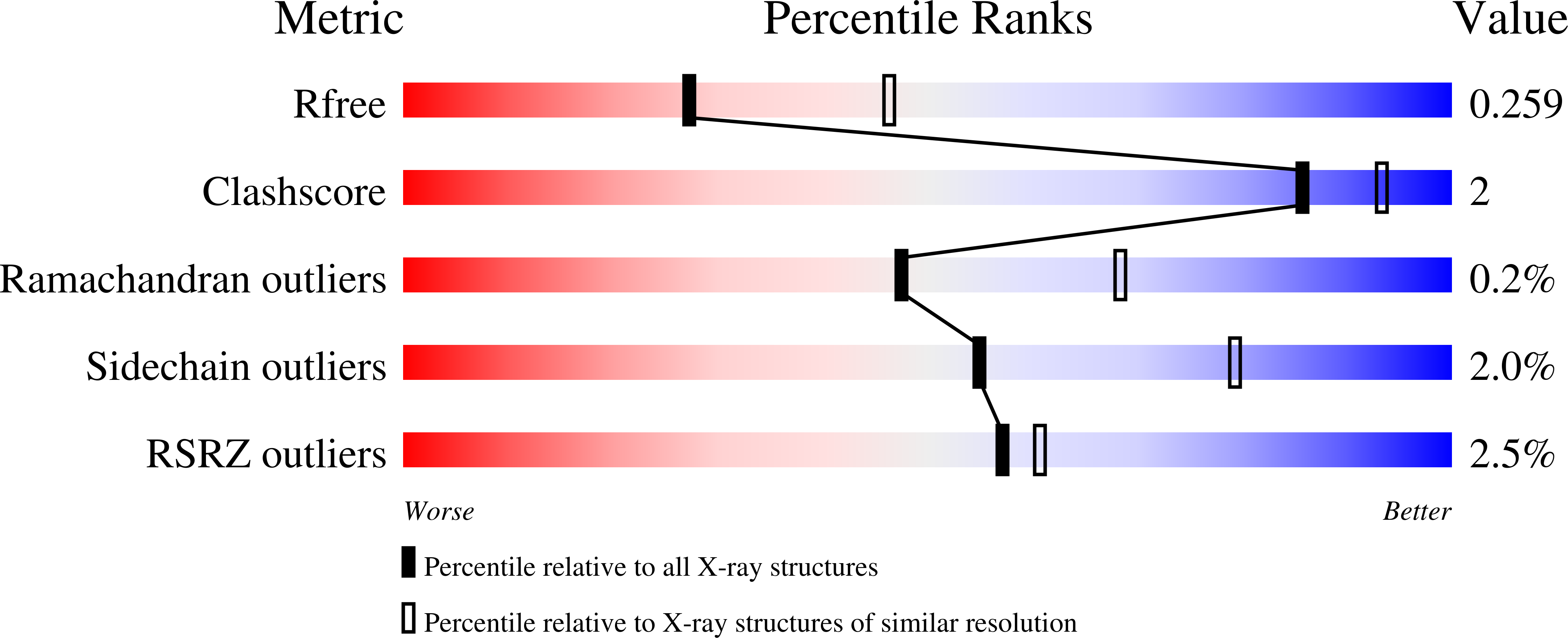
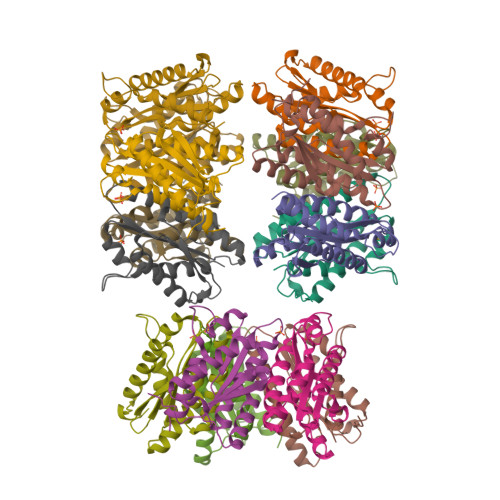
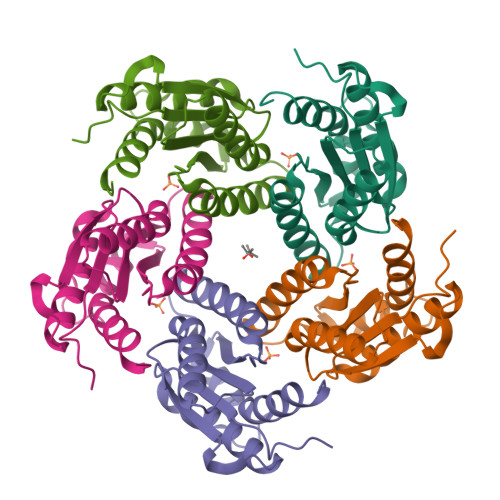
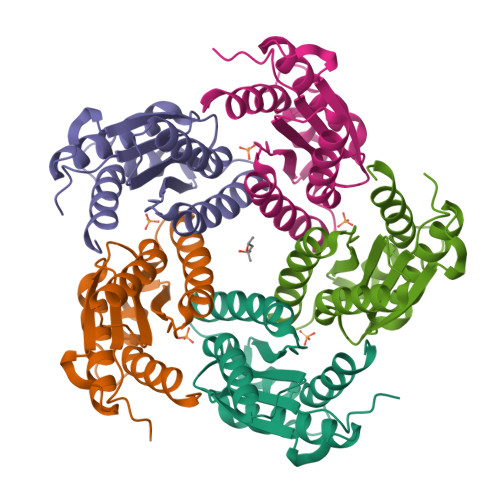
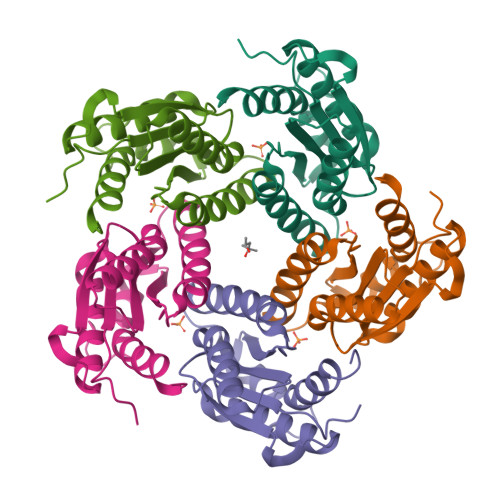
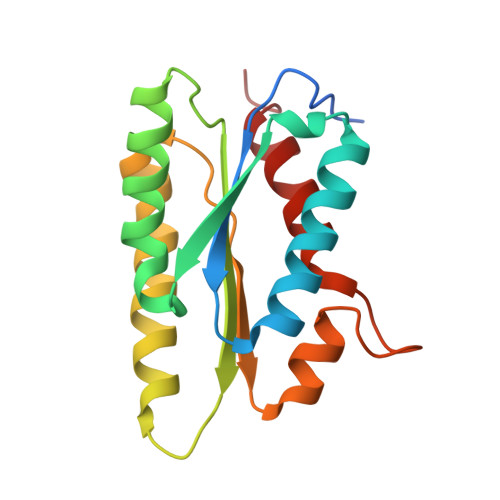
Lumazine synthase is an enzyme involved in riboflavin biosynthesis in many plants and microorganisms, including numerous human pathogens. The fact that the enzymes of the riboflavin biosynthesis pathway are not present in the human or animal host makes them potential targets for anti-infective agents. The crystal structure of lumazine synthase from Candida albicans was solved by molecular replacement and refined at 2.5-Angstrom resolution. The results of crystallographic investigations and sedimentation equilibrium experiments clearly indicated the presence of pentameric assemblies of the enzyme either in crystals or in solution. Isothermal titration calorimetry measurements of the binding reactions of four different inhibitors revealed high affinity for all four compounds with binding constants in the micromolar range. Structural comparison with previously determined structures of the enzyme.ligand complexes of other orthologue allowed modeling of the binding of four different inhibitors into the active site of lumazine synthase from Candida albicans.
Organizational Affiliation:
Karolinska Institutet, NOVUM, Centre for Structural Biochemistry, Halsovagen 7-9, S-14157 Huddinge, Sweden. katja.morgunova@biosci.ki.se