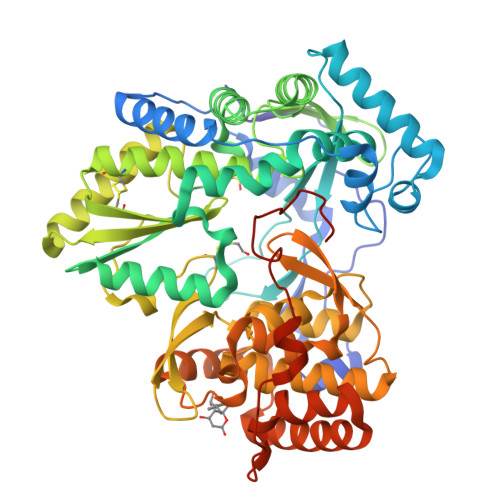
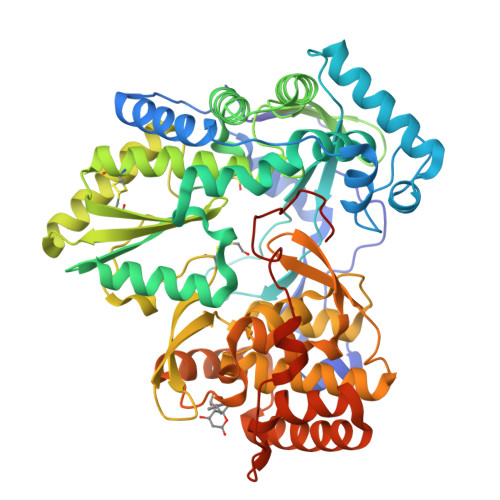
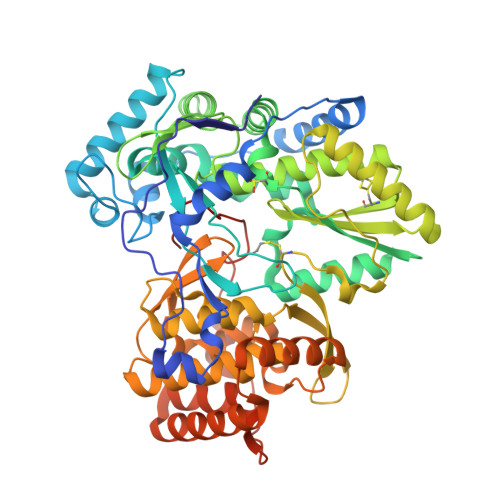
Identification and structure-based optimization of novel dihydropyrones as potent HCV RNA polymerase inhibitors.
Li, H., Tatlock, J., Linton, A., Gonzalez, J., Borchardt, A., Dragovich, P., Jewell, T., Prins, T., Zhou, R., Blazel, J., Parge, H., Love, R., Hickey, M., Doan, C., Shi, S., Duggal, R., Lewis, C., Fuhrman, S.(2006) Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16: 4834-4838
- PubMed: 16824756
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2006.06.065
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2HAI - PubMed Abstract:
A novel class of non-nucleoside HCV NS5B polymerase inhibitors has been identified from screening. A co-crystal structure revealed an allosteric binding site in the protein that required a unique conformational change to accommodate inhibitor binding. Herein we report the structure-activity relationships (SARs) of this novel class of dihydropyrone-containing compounds that show potent inhibitory activities against the HCV RNA polymerase in biochemical assays.
Organizational Affiliation:
Pfizer Global Research and Development, La Jolla Laboratories, 10770 Science Center Dr., San Diego, CA 92121, USA. hui.li@pfizer.com