N-Phosphonacetyl-l-isoasparagine a Potent and Specific Inhibitor of Escherichia coli Aspartate Transcarbamoylase.
Eldo, J., Cardia, J.P., O'day, E.M., Xia, J., Tsuruta, H., Kantrowitz, E.R.(2006) J Med Chem 49: 5932-5938
- PubMed: 17004708
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm0607294
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2H3E - PubMed Abstract:
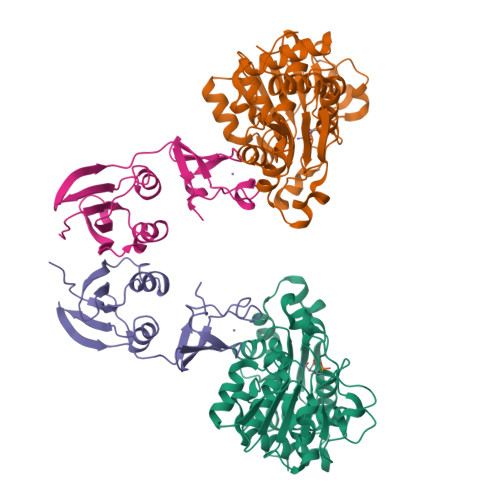
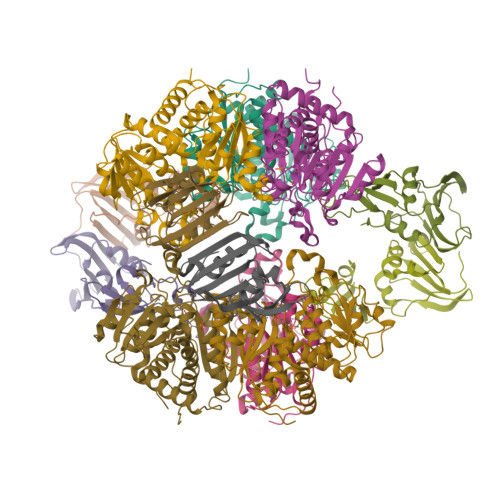
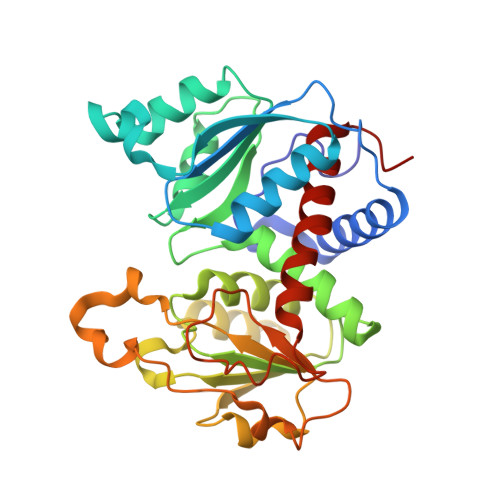
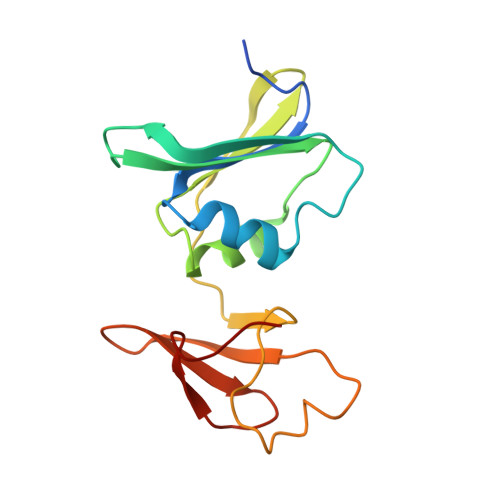
The synthesis of a new inhibitor, N-phosphonacetyl-L-isoasparagine (PALI), of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATCase) is reported, as well as structural studies of the enzyme.PALI complex. PALI was synthesized in 7 steps from beta-benzyl L-aspartate. The KD of PALI was 2 microM. Kinetics and small-angle X-ray scattering experiments showed that PALI can induce the cooperative transition of ATCase from the T to the R state. The X-ray structure of the enzyme.PALI complex showed 22 hydrogen-bonding interactions between the enzyme and PALI. The kinetic characterization and crystal structure of the ATCase.PALI complex also provides detailed information regarding the importance of the alpha-carboxylate for the binding of the substrate aspartate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Merkert Chemistry Center, Boston College, Chestnut Hill, Massachussetts 02467-3808, USA.