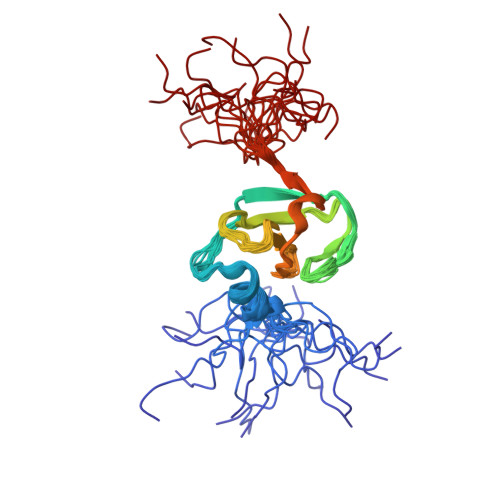
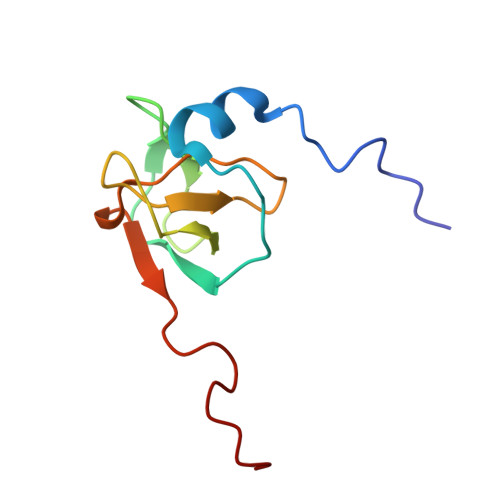
Redox-Regulated Conformational Changes in an SH3 Domain
Zimmermann, J., Kuhne, R., Sylvester, M., Freund, C.(2007) Biochemistry 46: 6971-6977
- PubMed: 17511475
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi700437r
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2GTJ, 2GTO - PubMed Abstract:
Oxidation-induced conformational changes in proteins provide a powerful mechanism to sense the redox state of a living cell. In contrast to the unspecific and often irreversible oxidation of intracellular proteins during severe oxidative stress, regulatory redox events need to have specific and transient effects on cellular targets. Here we present evidence for the reversible formation of a vicinal disulfide bond in a prototypic protein interaction domain. NMR spectroscopy was used to determine the structure of the N-terminal hSH3 domain (hSH3N) of the immune cell protein ADAP (adhesion and degranulation promoting adapter protein) in the reduced and oxidized states. An eight-membered ring formed upon oxidation of two neighboring cysteines leads to significant changes in the variable arginine-threonine (RT) loop of the hSH3N domain and alters the helix-sheet packing of the domain. The redox potential for this structural transition is -228 mV at pH 7.4. This is compatible with a role of the cysteinylcysteine moiety in redox signaling during T cell activation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Protein Engineering Group, Leibniz-Institut für Molekulare Pharmakologie und Freie Universität Berlin, 13125 Berlin, Germany.