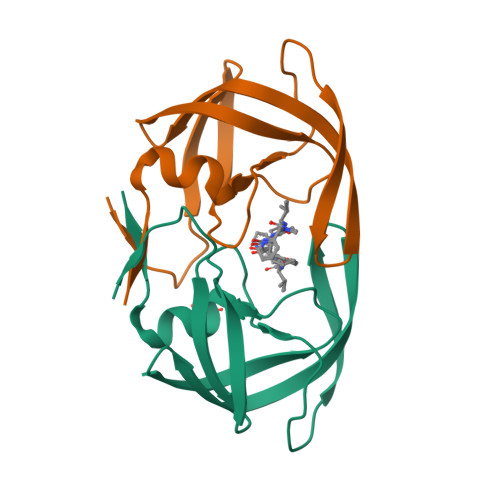
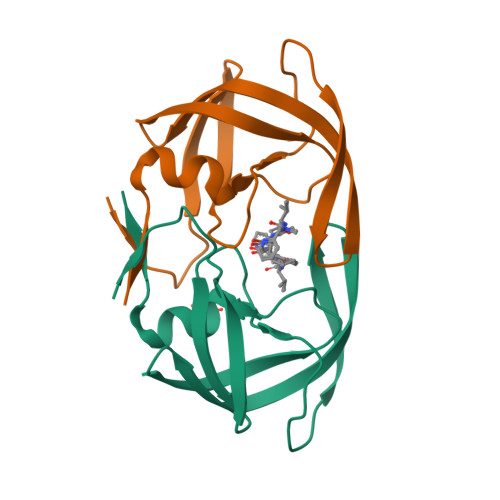
Design, synthesis, evaluation, and crystallographic-based structural studies of HIV-1 protease inhibitors with reduced response to the V82A mutation.
Clemente, J.C., Robbins, A., Grana, P., Paleo, M.R., Correa, J.F., Villaverde, M.C., Sardina, F.J., Govindasamy, L., Agbandje-McKenna, M., McKenna, R., Dunn, B.M., Sussman, F.(2008) J Med Chem 51: 852-860
- PubMed: 18215016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm701170f
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FLE - PubMed Abstract:
In our quest for HIV-1 protease inhibitors that are not affected by the V82A resistance mutation, we have synthesized and tested a second generation set of C2-symmetric HIV-1 protease inhibitors that contain a cyclohexane group at P1 and/or P1'. The binding affinity results indicate that these compounds have an improved response to the appearance of the V82A mutation than the parent compound. The X-ray structure of one of these compounds with the V82A HIV-1 PR variant provides the structural rationale for the better resistance profile of these compounds. Moreover, scrutiny of the X-ray structure suggests that the ring of the Cha side chain might be in a boat rather than in the chair conformation, a result supported by molecular dynamics simulations.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Florida College of Medicine, Gainesville, Florida 32610, USA.