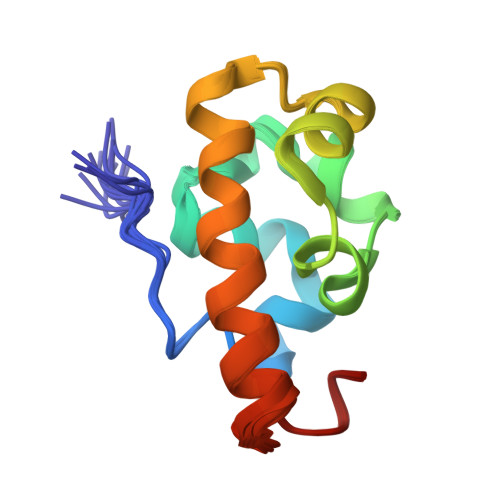
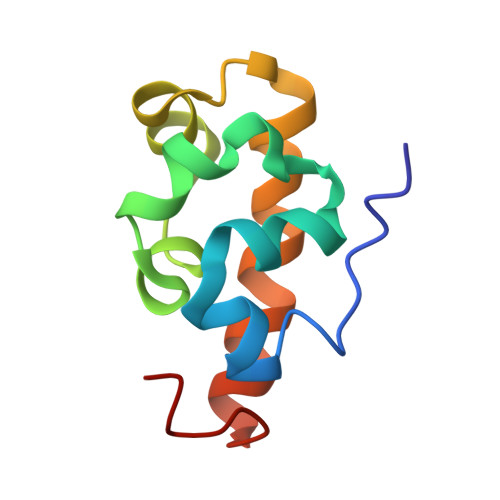
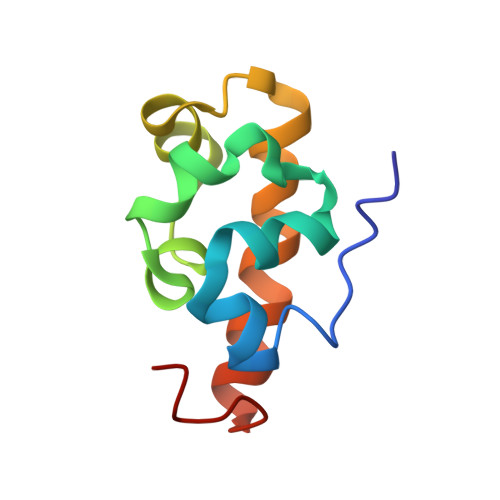
Solution Structure of the Vts1 SAM Domain in the Presence of RNA.
Edwards, T.A., Butterwick, J.A., Zeng, L., Gupta, Y.K., Wang, X., Wharton, R.P., Palmer, A.G., Aggarwal, A.K.(2006) J Mol Biology 356: 1065-1072
- PubMed: 16405996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.004
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2FE9 - PubMed Abstract:
The yeast Vts1 SAM (sterile alpha motif) domain is a member of a new class of SAM domains that specifically bind RNA. To elucidate the structural basis for RNA binding, the solution structure of the Vts1 SAM domain, in the presence of a specific target RNA, has been solved by multidimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. The Vts1 SAM domain retains the "core" five-helix-bundle architecture of traditional SAM domains, but has additional short helices at N and C termini, comprising a small substructure that caps the core helices. The RNA-binding surface of Vts1, determined by chemical shift perturbation, maps near the ends of three of the core helices, in agreement with mutational data and the electrostatic properties of the molecule. These results provide a structural basis for the versatility of the SAM domain in protein and RNA-recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Structural Biology Program, Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Mount Sinai School of Medicine, Box 1677, 1425 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10029, USA.