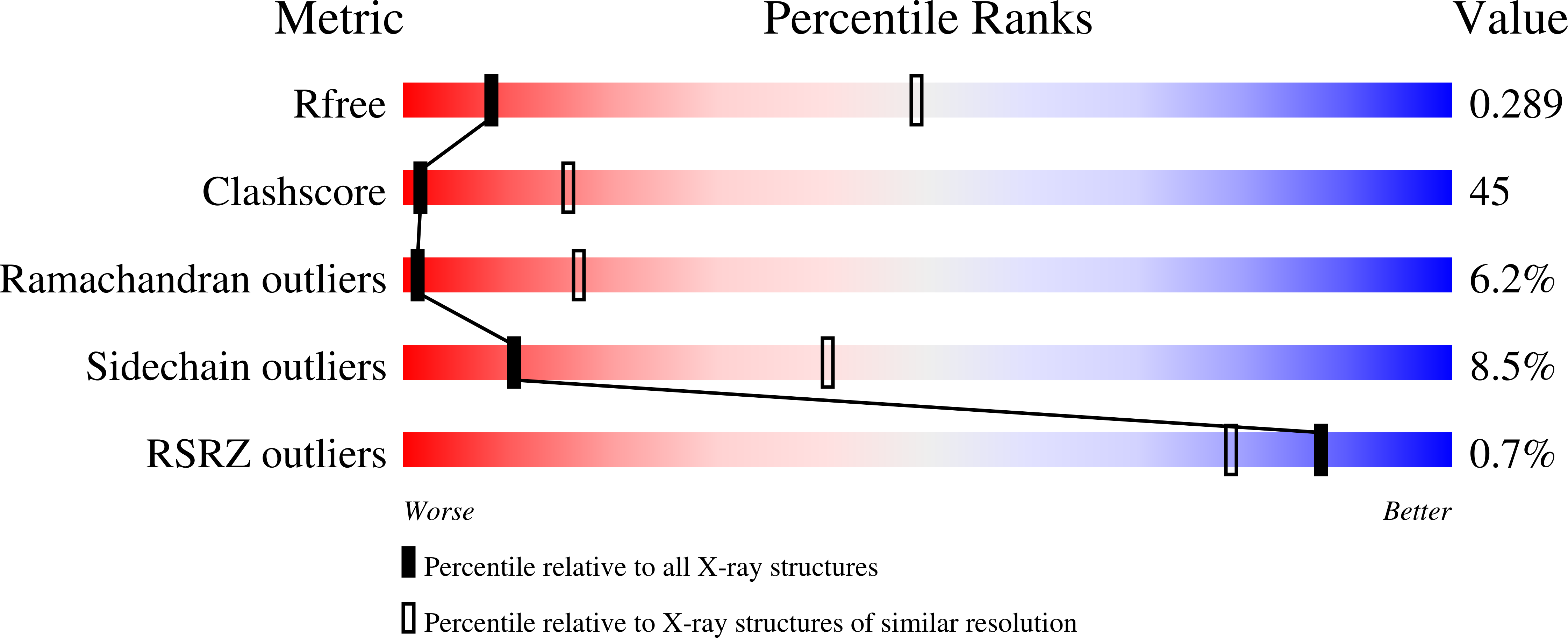
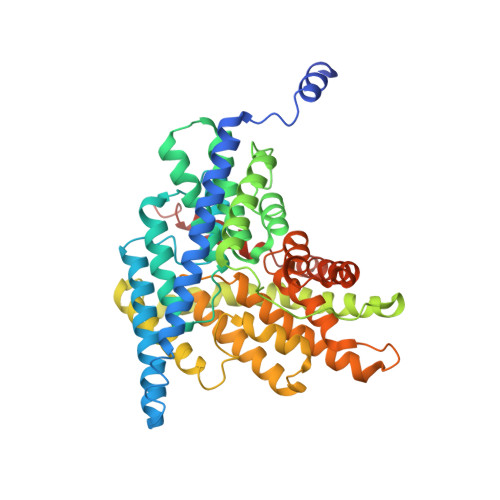
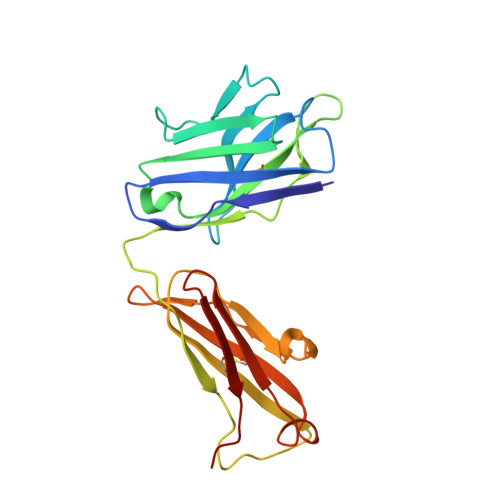
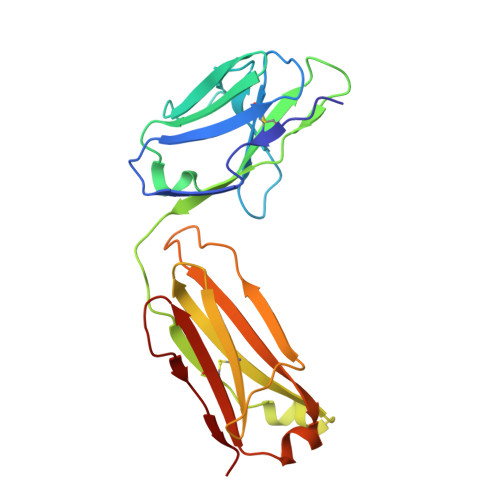
Ion-binding properties of the ClC chloride selectivity filter.
Lobet, S., Dutzler, R.(2006) EMBO J 25: 24-33
- PubMed: 16341087
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600909
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2EXW, 2EXY, 2EZ0 - PubMed Abstract:
The ClC channels are members of a large protein family of chloride (Cl-) channels and secondary active Cl- transporters. Despite their diverse functions, the transmembrane architecture within the family is conserved. Here we present a crystallographic study on the ion-binding properties of the ClC selectivity filter in the close homolog from Escherichia coli (EcClC). The ClC selectivity filter contains three ion-binding sites that bridge the extra- and intracellular solutions. The sites bind Cl- ions with mM affinity. Despite their close proximity within the filter, the three sites can be occupied simultaneously. The ion-binding properties are found conserved from the bacterial transporter EcClC to the human Cl- channel ClC-1, suggesting a close functional link between ion permeation in the channels and active transport in the transporters. In resemblance to K+ channels, ions permeate the ClC channel in a single file, with mutual repulsion between the ions fostering rapid conduction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland.