Investigation of the functional role of tryptophan-22 in Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase by site-directed mutagenesis.
Warren, M.S., Brown, K.A., Farnum, M.F., Howell, E.E., Kraut, J.(1991) Biochemistry 30: 11092-11103
- PubMed: 1932031
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00110a011
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DRC, 3DRC - PubMed Abstract:
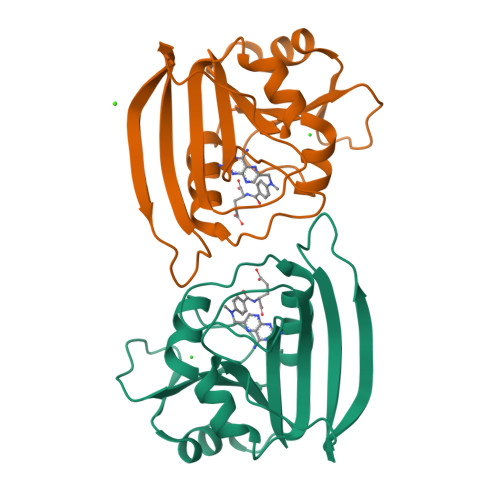
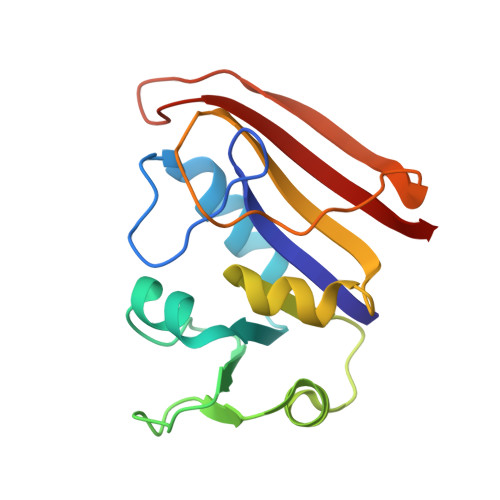
We have applied site-directed mutagenesis methods to change the conserved tryptophan-22 in the substrate binding site of Escherichia coli dihydrofolate reductase to phenylalanine (W22F) and histidine (W22H). The crystal structure of the W22F mutant in a binary complex with the inhibitor methotrexate has been refined at 1.9-A resolution. The W22F difference Fourier map and least-squares refinement show that structural effects of the mutation are confined to the immediate vicinity of position 22 and include an unanticipated 0.4-A movement of the methionine-20 side chain. A conserved bound water-403, suspected to play a role in the protonation of substrate DHF, has not been displaced by the mutation despite the loss of a hydrogen bond with tryptophan-22. Steady-state kinetics, stopped-flow kinetics, and primary isotope effects indicate that both mutations increase the rate of product tetrahydrofolate release, the rate-limiting step in the case of the wild-type enzyme, while slowing the rate of hydride transfer to the point where it now becomes at least partially rate determining. Steady-state kinetics show that below pH 6.8, kcat is elevated by up to 5-fold in the W22F mutant as compared with the wild-type enzyme, although kcat/Km(dihydrofolate) is lower throughout the observed pH range. For the W22H mutant, both kcat and kcat/Km(dihydrofolate) are substantially lower than the corresponding wild-type values. While both mutations weaken dihydrofolate binding, cofactor NADPH binding is not significantly altered. Fitting of the kinetic pH profiles to a general protonation scheme suggests that the proton affinity of dihydrofolate may be enhanced upon binding to the enzyme. We suggest that the function of tryptophan-22 may be to properly position the side chain of methionine-20 with respect to N5 of the substrate dihydrofolate.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla 92093.