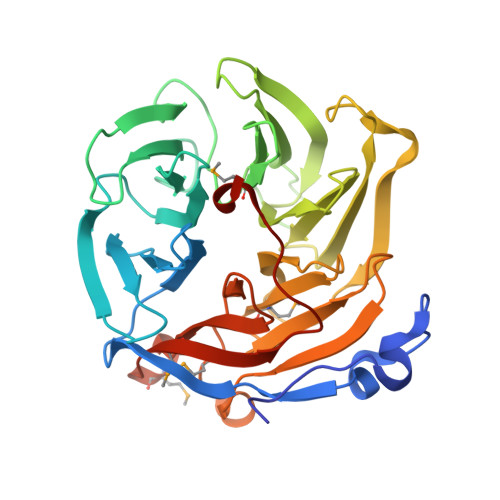
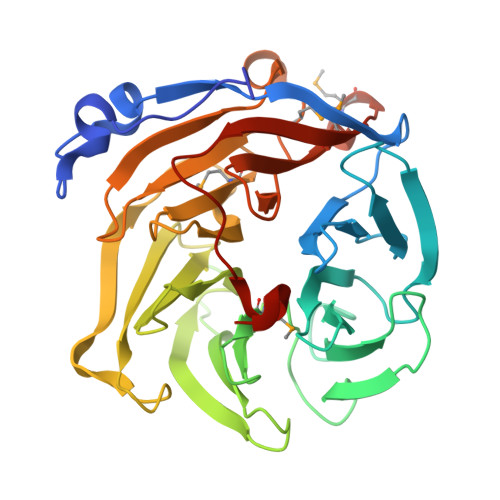
Structural and Mutational Analyses of Drp35 from Staphylococcus aureus: A POSSIBLE MECHANISM FOR ITS LACTONASE ACTIVITY
Tanaka, Y., Morikawa, K., Ohki, Y., Yao, M., Tsumoto, K., Watanabe, N., Ohta, T., Tanaka, I.(2007) J Biological Chem 282: 5770-5780
- PubMed: 17166853
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607340200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DG0, 2DG1, 2DSO - PubMed Abstract:
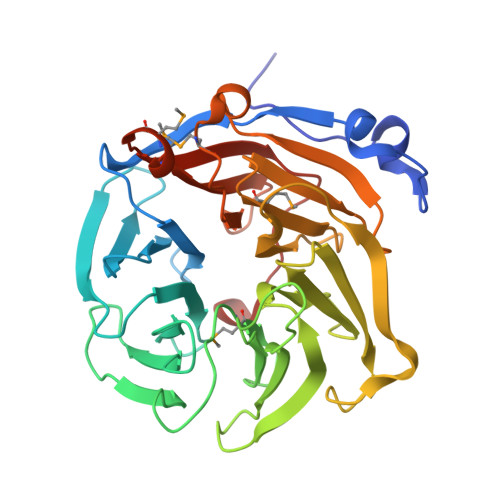
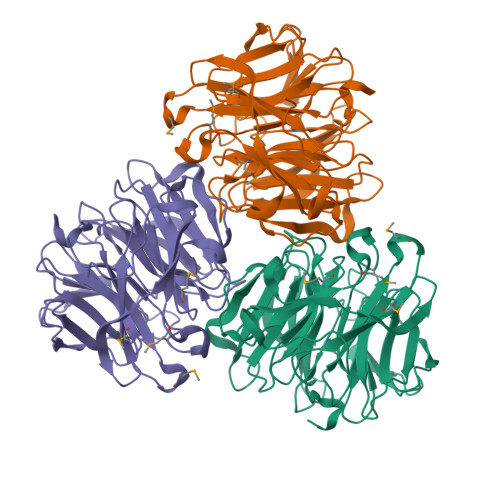
Drp35 is a protein induced by cell wall-affecting antibiotics or detergents; it possesses calcium-dependent lactonase activity. To determine the molecular basis of the lactonase activity, we first solved the crystal structures of Drp35 with and without Ca(2+); these showed that the molecule has a six-bladed beta-propeller structure with two calcium ions bound at the center of the beta-propeller and surface region. Mutational analyses of evolutionarily conserved residues revealed that the central calcium-binding site is essential for the enzymatic activity of Drp35. Substitution of some other amino acid residues for the calcium-binding residues demonstrated the critical contributions of Glu(48), Asp(138), and Asp(236) to the enzymatic activity. Differential scanning calorimetric analysis revealed that the loss of activity of E48Q and D236N, but not D138N, was attributed to their inability to hold the calcium ion. Further structural analysis of the D138N mutant indicates that it lacks a water molecule bound to the calcium ion rather than the calcium ion itself. Based on these observations and structural information, a possible catalytic mechanism in which the calcium ion and its binding residues play direct roles was proposed for the lactonase activity of Drp35.
Organizational Affiliation:
Faculty of Advanced Life Sciences, Hokkaido University, Sapporo 060-0810, Japan.