Structural basis for red-shifted emission of a GFP-like protein from the marine copepod Chiridius poppei
Suto, K., Masuda, H., Takenaka, Y., Tsuji, F.I., Mizuno, H.(2009) Genes Cells 14: 727-737
- PubMed: 19469881
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2443.2009.01305.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2DD7, 2DD9 - PubMed Abstract:
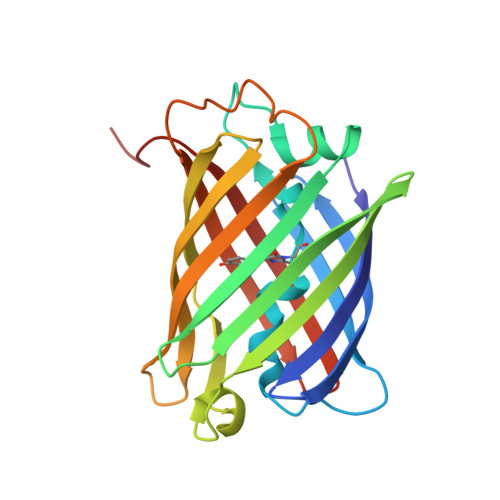
The fluorescence excitation and emission maxima of a GFP-like protein from the marine copepod Chiridius poppei (CpYGFP) show a significant red shift (lambda(ex) = 509 nm, lambda(em) = 517 nm) compared with those of GFP from Aequorea victoria (avGFP) and other GFP-like proteins from marine copepods. We performed crystallographic and biochemical studies to understand why this shift occurs in CpYGFP. The structure of CpYGFP showed that the imidazole side chain of His52 is involved in stacking on the phenol moiety of the chromophore. We investigated the potential role of His52 in causing the red-shifted spectral properties by performing mutational analyses of H52T, H52D and H52F. The emission wavelengths of H52T and H52D were blue-shifted and that of H52F was red-shifted relative to the wild type. Comparison of its structure of another copepod GFP (ppluGFP2) having an emission maximum at 502 nm showed that the imidazole ring of His54 (corresponding to His52 in CpYGFP) is flipped out of the stacking position with the chromophore. These findings suggest that pi-pi stacking interaction between His52 and the phenol moiety of the chromophore is the likely cause of the red-shift in light emission.
Organizational Affiliation:
VALWAY Technology Center, NEC Soft, Ltd, 1-18-7, Shinkiba, Koto-ku, Tokyo 136-8627, Japan.