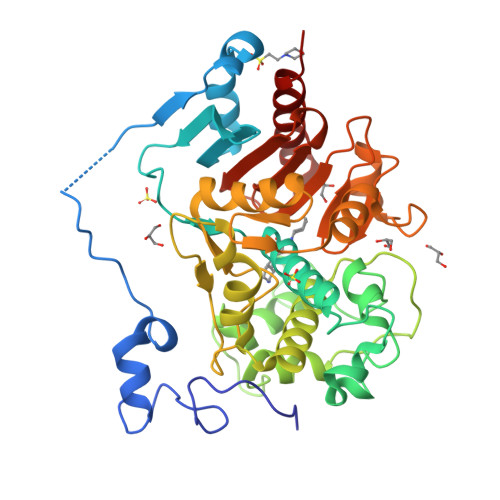
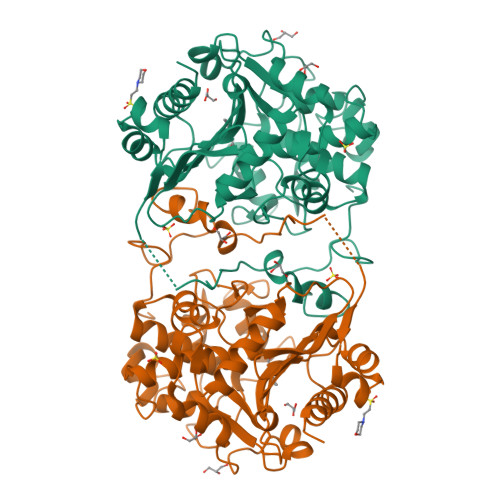
Nylon-oligomer degrading enzyme/substrate complex: catalytic mechanism of 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase
Negoro, S., Ohki, T., Shibata, N., Sasa, K., Hayashi, H., Nakano, H., Yasuhira, K., Kato, D., Takeo, M., Higuchi, Y.(2007) J Mol Biology 370: 142-156
- PubMed: 17512009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2007.04.043
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WYC, 2DCF - PubMed Abstract:
We performed X-ray crystallographic analyses of 6-aminohexanoate-dimer hydrolase (Hyb-24DN), an enzyme responsible for the degradation of nylon-6, an industry by-product, and of a complex between Hyb-24DN-A(112) (S112A-mutant of Hyb-24DN) and 6-aminohexanoate-linear dimer (Ald) at 1.58 A and 1.4 A resolution, respectively. In Hyb-24DN, Asp181-O(delta) forms hydrogen bonds with Tyr170-O(eta), -two of the catalytic and binding amino acids, and a loop between Asn167 and Val177. This state is the so-called open form, allowing its substrate to bind in the space between the loop and catalytic residues. Upon substrate binding (in Hyb-24DN-A(112)/Ald complex), the loop is shifted 4.3 A at Tyr170-C(alpha), and the side-chain of Tyr170 is rotated. By the combined effect, Tyr170-O(eta) moves a total of 10.5 A, resulting in the formation of hydrogen bonds with the nitrogen of amide linkage in Ald (closed form). In addition, electrostatic interaction between Asp181-O(delta) and the amino group in Ald stabilizes the substrate binding. We propose here that the enzyme catalysis proceeds according to the following steps: (i) Ald-induced transition from open to closed form, (ii) nucleophilic attack of Ser112 to Ald and formation of a tetrahedral intermediate, (iii) formation of acyl enzyme and transition to open form, (iv) deacylation. Amino acid substitutions reducing the enzyme/Ald interaction at positions 181 or 170 drastically decreased the Ald-hydrolytic activity, but had very little effect on esterolytic activity, suggesting that esterolytic reaction proceeds regardless of conversion. Present models illustrate why new activity against the nylon oligomer has evolved in an esterase with beta-lactamase folds, while retaining the original esterolytic functions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Materials Science and Chemistry, Graduate School of Engineering, University of Hyogo, 2167 Shosha, Himeji, Hyogo 671-2280, Japan. negoro@eng.u-hyogo.ac.jp