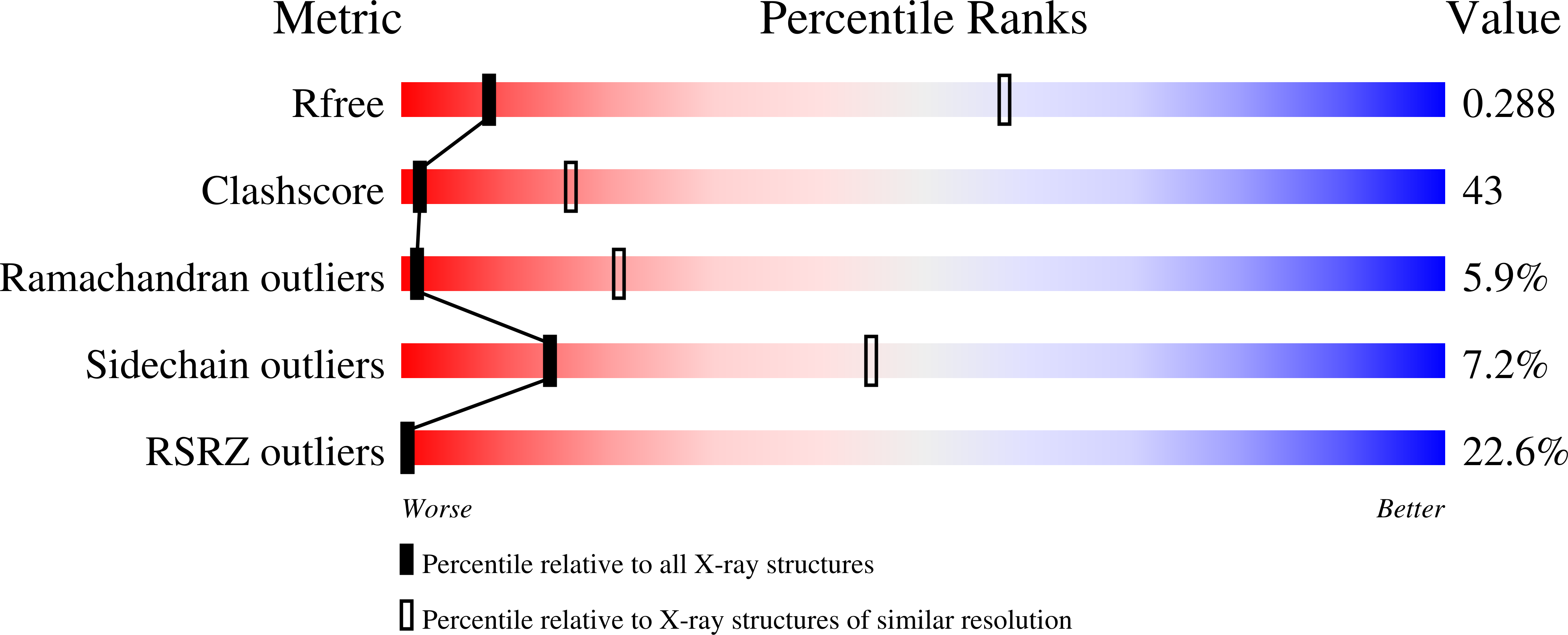
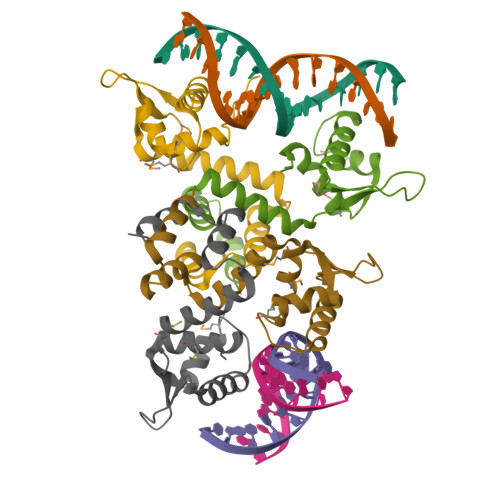
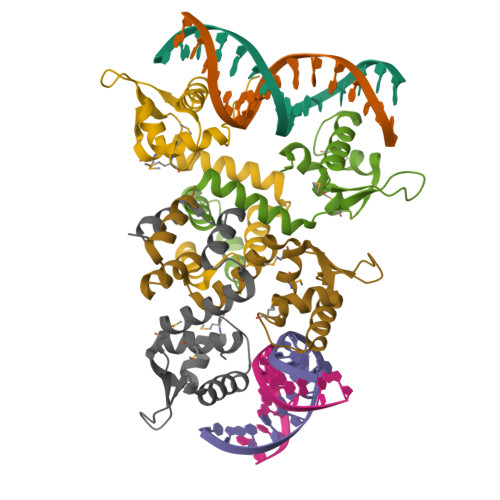
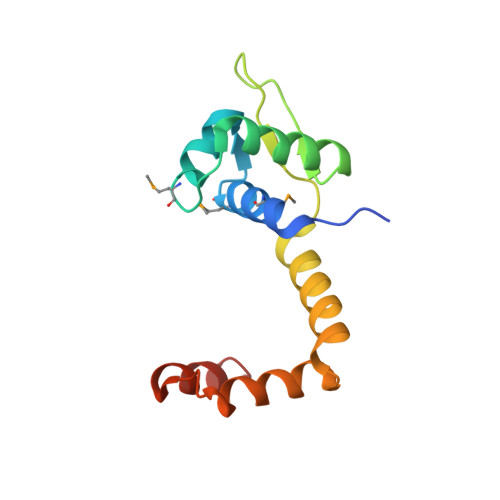
Structure of the MecI repressor from Staphylococcus aureus in complex with the cognate DNA operator of mec.
Safo, M.K., Ko, T.P., Musayev, F.N., Zhao, Q., Wang, A.H., Archer, G.L.(2006) Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62: 320-324
- PubMed: 16582476
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1744309106009742
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2D45 - PubMed Abstract:
The dimeric repressor MecI regulates the mecA gene that encodes the penicillin-binding protein PBP-2a in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). MecI is similar to BlaI, the repressor for the blaZ gene of beta-lactamase. MecI and BlaI can bind to both operator DNA sequences. The crystal structure of MecI in complex with the 32 base-pair cognate DNA of mec was determined to 3.8 A resolution. MecI is a homodimer and each monomer consists of a compact N-terminal winged-helix domain, which binds to DNA, and a loosely packed C-terminal helical domain, which intertwines with its counter-monomer. The crystal contains horizontal layers of virtual DNA double helices extending in three directions, which are separated by perpendicular DNA segments. Each DNA segment is bound to two MecI dimers. Similar to the BlaI-mec complex, but unlike the MecI-bla complex, the MecI repressors bind to both sides of the mec DNA dyad that contains four conserved sequences of TACA/TGTA. The results confirm the up-and-down binding to the mec operator, which may account for cooperative effect of the repressor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Medicinal Chemistry, School of Pharmacy and Institute for Structural Biology and Drug Discovery, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia 23298, USA. msafo@vcu.edu