Nup50/Npap60 Function in Nuclear Import Complex Disassembly and Importin Recycling
Matsuura, Y., Stewart, M.(2005) EMBO J 24: 3681
- PubMed: 16222336
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600843
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2C1M, 2C1T - PubMed Abstract:
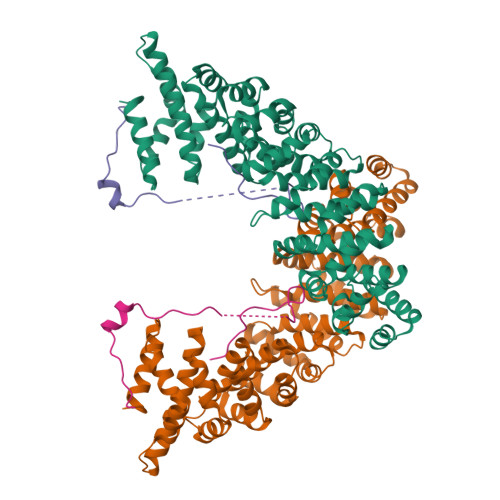
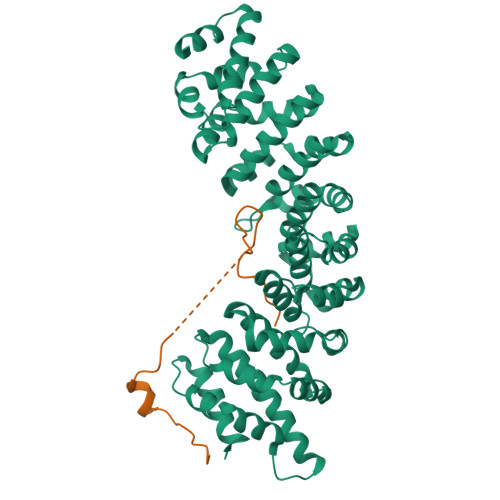
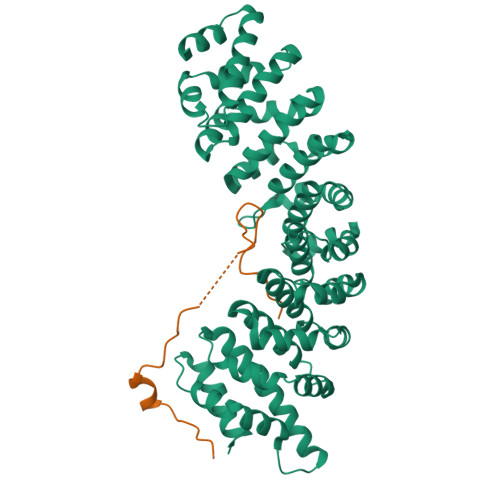
Nuclear import of proteins containing classical nuclear localization signals (NLS) is mediated by the importin-alpha:beta complex that binds cargo in the cytoplasm and facilitates its passage through nuclear pores, after which nuclear RanGTP dissociates the import complex and the importins are recycled. In vertebrates, import is stimulated by nucleoporin Nup50, which has been proposed to accompany the import complex through nuclear pores. However, we show here that the Nup50 N-terminal domain actively displaces NLSs from importin-alpha, which would be more consistent with Nup50 functioning to coordinate import complex disassembly and importin recycling. The crystal structure of the importin-alpha:Nup50 complex shows that Nup50 binds at two sites on importin-alpha. One site overlaps the secondary NLS-binding site, whereas the second extends along the importin-alpha C-terminus. Mutagenesis indicates that interaction at both sites is required for Nup50 to displace NLSs. The Cse1p:Kap60p:RanGTP complex structure suggests how Nup50 is then displaced on formation of the importin-alpha export complex. These results provide a rationale for understanding the series of interactions that orchestrate the terminal steps of nuclear protein import.
Organizational Affiliation:
MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology, Cambridge, UK.