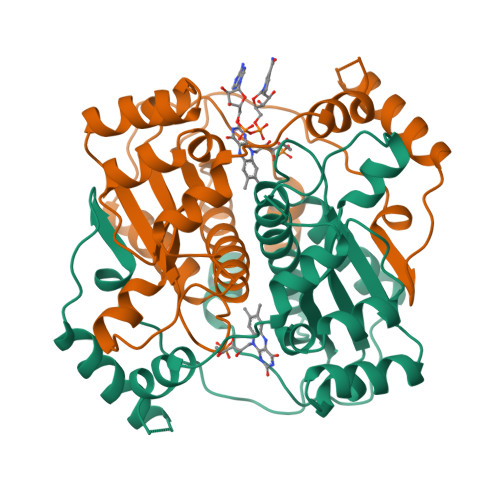
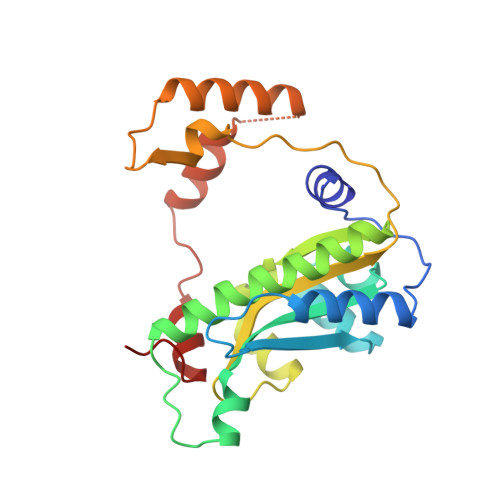
Unusual folded conformation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide bound to flavin reductase P.
Tanner, J.J., Tu, S.C., Barbour, L.J., Barnes, C.L., Krause, K.L.(1999) Protein Sci 8: 1725-1732
- PubMed: 10493573
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.8.9.1725
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2BKJ - PubMed Abstract:
The 2.1 A resolution crystal structure of flavin reductase P with the inhibitor nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) bound in the active site has been determined. NAD adopts a novel, folded conformation in which the nicotinamide and adenine rings stack in parallel with an inter-ring distance of 3.6 A. The pyrophosphate binds next to the flavin cofactor isoalloxazine, while the stacked nicotinamide/adenine moiety faces away from the flavin. The observed NAD conformation is quite different from the extended conformations observed in other enzyme/NAD(P) structures; however, it resembles the conformation proposed for NAD in solution. The flavin reductase P/NAD structure provides new information about the conformational diversity of NAD, which is important for understanding catalysis. This structure offers the first crystallographic evidence of a folded NAD with ring stacking, and it is the first enzyme structure containing an FMN cofactor interacting with NAD(P). Analysis of the structure suggests a possible dynamic mechanism underlying NADPH substrate specificity and product release that involves unfolding and folding of NADP(H).
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, University of Missouri-Columbia 65211, USA.