Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-aryl-4,5-dihydro-1h-pyraxolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one inhibitors of cyclin dependent kinases
Markwalder, J.A., Arnone, M.R., Benfield, P.A., Boisclair, M., Burton, C.R., Chang, C.-C., Cox, S.S., Czerniak, P.M., Dean, C.L., Dolenaik, D., Grafstrom, R., Harrison, B.A., Kaltenbach III, R.F., Nugiel, D.A., Rossi, K.A., Sherk, S.R., Sisk, L.M., Stouten, P., Trainor, G.L., Worland, P., Seitz, S.P.(2004) J Med Chem 47: 5894-5911
- PubMed: 15537345
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm020455u
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2B54 - PubMed Abstract:
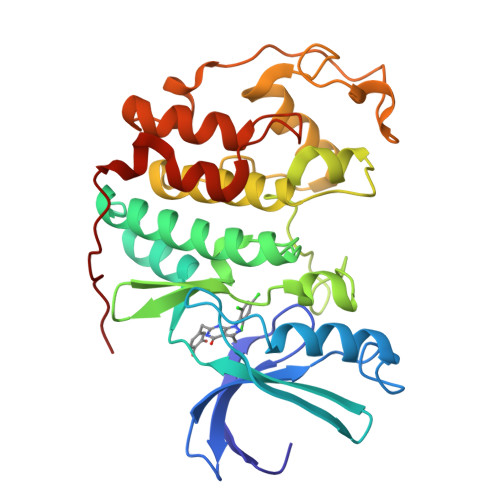
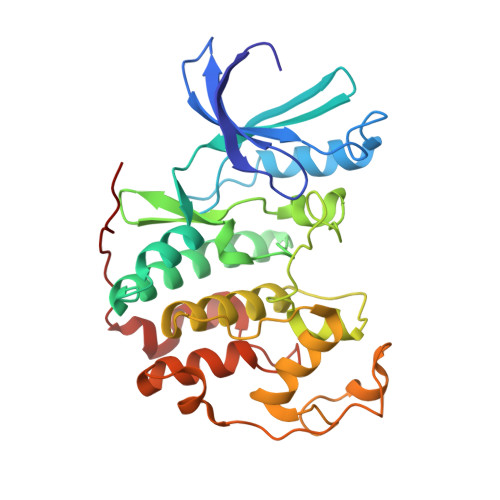
Using a high-throughput screening strategy, a series of 1-aryl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-ones was identified that inhibit the cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/cyclin D1 complex-mediated phosphorylation of a protein substrate with IC(50)s in the low micromolar range. On the basis of preliminary structure-activity relationships (SAR), a model was proposed in which these inhibitors occupy the ATP-binding site of the enzyme, forming critical hydrogen bonds to the same residue (Val96) to which the amino group in ATP is presumed to bind. X-ray diffraction studies on a later derivative bound to CDK2 support this binding mode. Iterative cycles of synthesis and screening lead to a novel series of potent, CDK2-selective 6-(arylmethyl)pyrazolopyrimidinones. Placement of a hydrogen-bond donor in the meta-position on the 6-arylmethyl group resulted in approximately 100-fold increases in CDK4 affinity, giving ligands that were equipotent inhibitors of CDK4 and CDK2. These compounds exhibit antiproliferative effects in the NCI HCT116 and other cell lines. The potency of these antiproliferative effects is enhanced in anilide derivatives and translates into tumor growth inhibition in a mouse xenograft model.
Organizational Affiliation:
Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharmaceutical Research Institute, Princeton, New Jersey 08543-4000, USA. jay.markwalder@bms.com