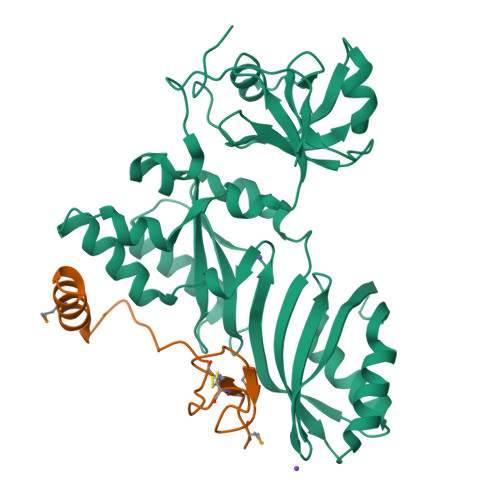
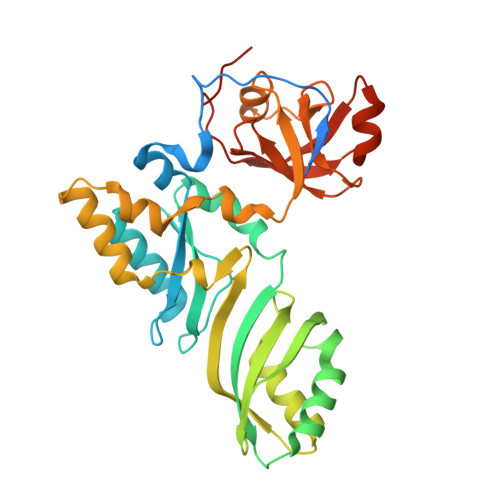
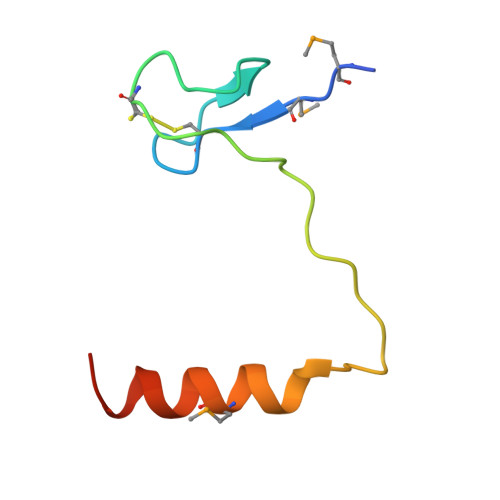
The Cbf5-Nop10 complex is a molecular bracket that organizes box H/ACA RNPs.
Hamma, T., Reichow, S.L., Varani, G., Ferre-D'Amare, A.R.(2005) Nat Struct Mol Biol 12: 1101-1107
- PubMed: 16286935
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb1036
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2APO, 2AQA, 2AQC - PubMed Abstract:
Box H/ACA ribonucleoprotein particles (RNPs) catalyze RNA pseudouridylation and direct processing of ribosomal RNA, and are essential architectural components of vertebrate telomerases. H/ACA RNPs comprise four proteins and a multihelical RNA. Two proteins, Cbf5 and Nop10, suffice for basal enzymatic activity in an archaeal in vitro system. We now report their cocrystal structure at 1.95-A resolution. We find that archaeal Cbf5 can assemble with yeast Nop10 and with human telomerase RNA, consistent with the high sequence identity of the RNP components between archaea and eukarya. Thus, the Cbf5-Nop10 architecture is phylogenetically conserved. The structure shows how Nop10 buttresses the active site of Cbf5, and it reveals two basic troughs that bidirectionally extend the active site cleft. Mutagenesis results implicate an adjacent basic patch in RNA binding. This tripartite RNA-binding surface may function as a molecular bracket that organizes the multihelical H/ACA and telomerase RNAs.
Organizational Affiliation:
Division of Basic Sciences, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, Seattle, Washington 98109-1024, USA.