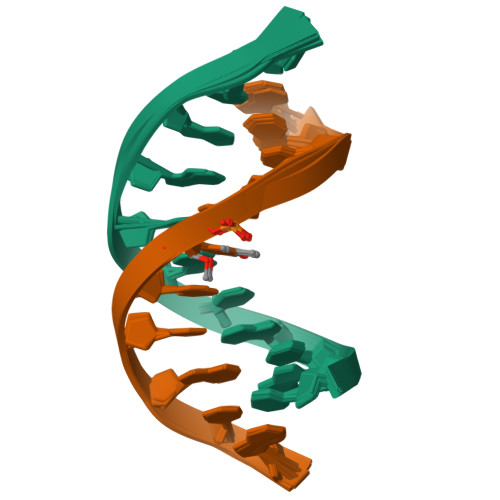
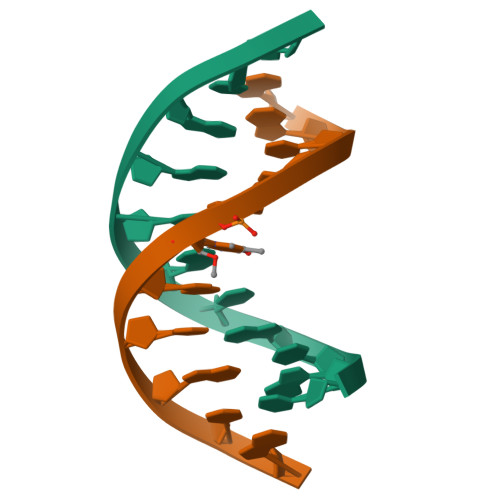
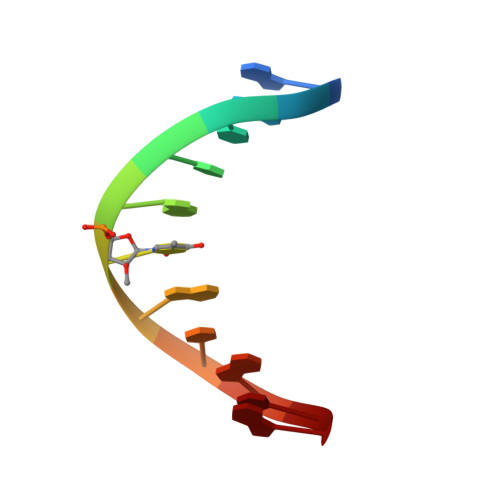
Structure of a DNA duplex containing a single 2'-O-methyl-beta-D-araT: combined use of NMR, restrained molecular dynamics, and full relaxation matrix refinement.
Gotfredsen, C.H., Spielmann, H.P., Wengel, J., Jacobsen, J.P.(1996) Bioconjug Chem 7: 680-688
- PubMed: 8950487
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bc960061f
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
214D - PubMed Abstract:
Two-dimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy was used to determine the solution structure of the double-stranded DNA oligonucleotide d(5'-CGCATATAGCC-3'): d(5'-GGCTAXATGCG-3'), where X is 1-(2-O-methyl-beta-D-arabinofuranosyl)thymine. The structure determination was based on a total relaxation matrix analysis of NOESY cross-peak intensities using the MARDIGRAS program. The improved RANDMARDI procedure was used during the calculations to include the experimental "noise" in the NOESY spectra. The NOE-derived distance restraints were applied in restrained molecular dynamics calculations. Twenty final structures each were generated for the modified DNA duplex from both A-form and B-form DNA starting structures. The root-mean-square deviation of the coordinates for the 40 structures was 0.82 A. The duplex adopts a normal B-DNA-type helix, and the spectra as well as the structure show that the modified nucleotide X adopts a C2'-endo (S) sugar conformation. There are no significant changes in the helix originating from the modified nucleotide. The CH3O group on X is directed toward the major groove, and there seems to be free space for further modifications at this position.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Odense University, Denmark.