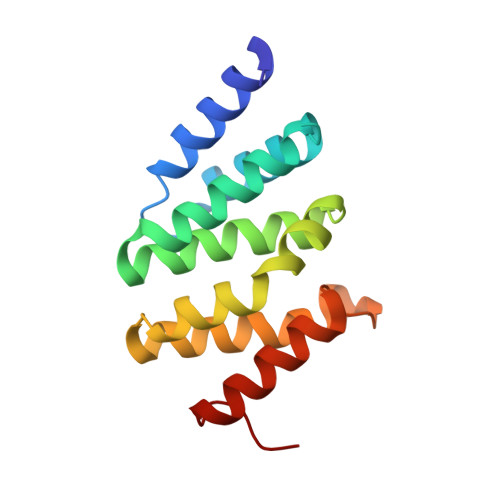
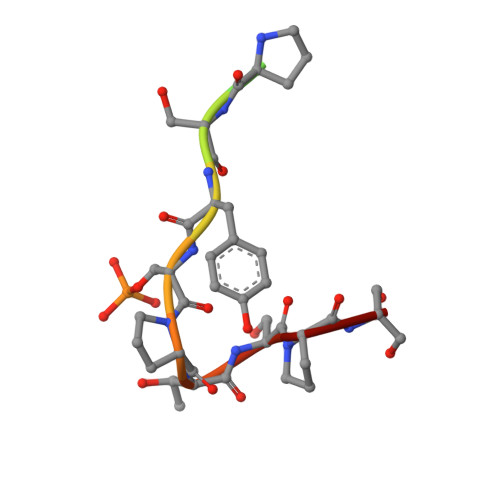
Recognition of RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain by 3'-RNA-processing factors.
Meinhart, A., Cramer, P.(2004) Nature 430: 223-226
- PubMed: 15241417
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02679
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SZ9, 1SZA - PubMed Abstract:
During transcription, RNA polymerase (Pol) II synthesizes eukaryotic messenger RNA. Transcription is coupled to RNA processing by the carboxy-terminal domain (CTD) of Pol II, which consists of up to 52 repeats of the sequence Tyr 1-Ser 2-Pro 3-Thr 4-Ser 5-Pro 6-Ser 7 (refs 1, 2). After phosphorylation, the CTD binds tightly to a conserved CTD-interacting domain (CID) present in the proteins Pcf11 and Nrd1, which are essential and evolutionarily conserved factors for polyadenylation-dependent and -independent 3'-RNA processing, respectively. Here we describe the structure of a Ser 2-phosphorylated CTD peptide bound to the CID domain of Pcf11. The CTD motif Ser 2-Pro 3-Thr 4-Ser 5 forms a beta-turn that binds to a conserved groove in the CID domain. The Ser 2 phosphate group does not make direct contact with the CID domain, but may be recognized indirectly because it stabilizes the beta-turn with an additional hydrogen bond. Iteration of the peptide structure results in a compact beta-spiral model of the CTD. The model suggests that, during the mRNA transcription-processing cycle, compact spiral regions in the CTD are unravelled and regenerated in a phosphorylation-dependent manner.
- Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, Gene Center, University of Munich, 81377 Munich, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: