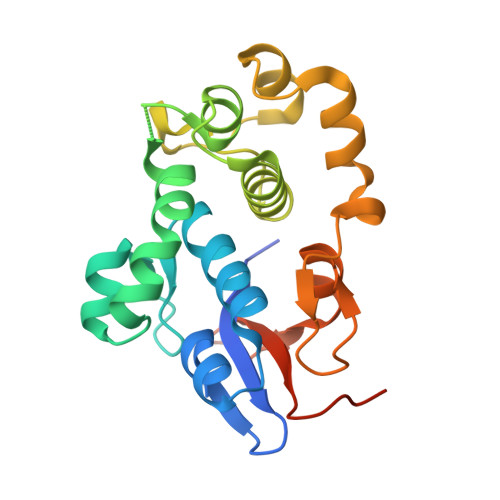
Structures of two intermediate filament-binding fragments of desmoplakin reveal a unique repeat motif structure.
Choi, H.J., Park-Snyder, S., Pascoe, L.T., Green, K.J., Weis, W.I.(2002) Nat Struct Biol 9: 612-620
- PubMed: 12101406
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb818
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LM5, 1LM7 - PubMed Abstract:
Desmosomes are intercellular junctions in which cadherin cell adhesion molecules are linked to the intermediate filament (IF) system. Desmoplakin is a member of the plakin family of IF-binding proteins. The C-terminal domain of desmoplakin (DPCT) mediates binding to IFs in desmosomes. The DPCT sequence contains three regions, termed A, B and C, consisting of 4.5 copies of a 38-amino acid repeat motif. We demonstrate that these regions form discrete subdomains that bind to IFs and report the crystal structures of domains B and C. In contrast to the elongated structures formed by other kinds of repeat motifs, the plakin repeats form a globular structure with a unique fold. A conserved basic groove found on the domain may represent an IF-binding site.
- Department of Structural Biology, Stanford University School of Medicine, 299 Campus Drive West, Stanford, California 94305, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: