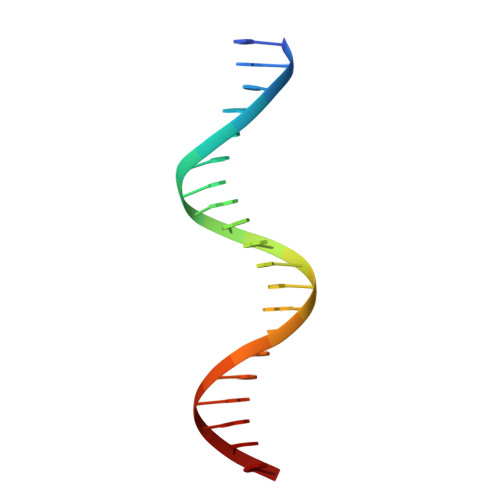
Crystal structure of the heterodimeric bZIP transcription factor c-Fos-c-Jun bound to DNA.
Glover, J.N., Harrison, S.C.(1995) Nature 373: 257-261
- PubMed: 7816143
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373257a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1FOS - PubMed Abstract:
The Fos and Jun families of eukaryotic transcription factors heterodimerize to form complexes capable of binding 5'-TGAGTCA-3' DNA elements. We have determined the X-ray crystal structure of a heterodimer of the bZIP regions of c-Fos and c-Jun bound to DNA. Both subunits form continuous alpha-helices. The carboxy-terminal regions form an asymmetric coiled-coil, and the amino-terminal regions make base-specific contacts with DNA in the major groove. Comparison of the two crystallographically distinct protein-DNA complexes show that the coiled-coil is flexibly joined to the basic regions and that the Fos-Jun heterodimer does not recognize the asymmetric 5'-TGAGTCA-3' recognition element in a unique orientation. There is an extensive network of electrostatic interactions between subunits within the coiled-coil, consistent with proposals that these interactions determine preferential formation of the heterodimer over either of the homodimers.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138.
Organizational Affiliation: