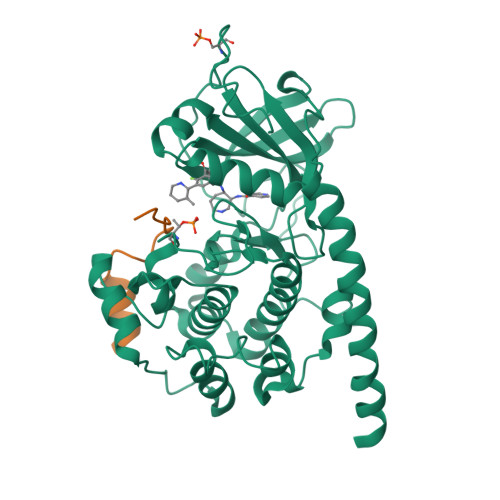
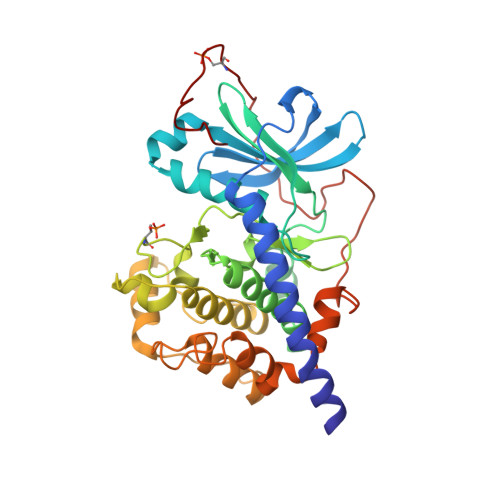
Design and crystal structures of protein kinase B-selective inhibitors in complex with protein kinase A and mutants
Breitenlechner, C.B., Friebe, W.-G., Brunet, E., Werner, G., Graul, K., Thomas, U., Kuenkele, K.-P., Schaefer, W., Gassel, M., Bossemeyer, D., Huber, R., Engh, R.A., Masjost, B.(2005) J Med Chem 48: 163-170
- PubMed: 15634010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/jm049701n
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1XH4, 1XH5, 1XH6, 1XH7, 1XH8, 1XH9, 1XHA - PubMed Abstract:
Protein kinase B (PKB)-selective inhibitors were designed, synthesized, and cocrystallized using the AGC kinase family protein kinase A (PKA, often called cAMP-dependent protein kinase); PKA has been used as a surrogate for other members of this family and indeed for protein kinases in general. The high homology between PKA and PKB includes very similar ATP binding sites and hence similar binding pockets for inhibitors, with only few amino acids that differ between the two kinases. A series of these sites were mutated in PKA in order to improve the surrogate model for a design of PKB-selective inhibitors. Namely, the PKA to PKB exchanges F187L and Q84E enable the design of the selective inhibitors described herein which mimic ATP but extend further into a site not occupied by ATP. In this pocket, selectivity over PKA can be achieved by the introduction of bulkier substituents. Analysis of the cocrystal structures and binding studies were performed to rationalize the selectivity and improve the design.
Organizational Affiliation:
Abteilung Strukturforschung, Max-Planck-Institut fuer Biochemie, 82152 Martinsried, Germany.