Crystallographic Evidence That the Dinuclear Copper Center of Tyrosinase Is Flexible during Catalysis
Matoba, Y., Kumagai, T., Yamamoto, A., Yoshitsu, H., Sugiyama, M.(2006) J Biol Chem 281: 8981-8990
- PubMed: 16436386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M509785200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WX2, 1WX4, 1WX5, 1WXC, 2AHK, 2AHL, 2ZMX - PubMed Abstract:
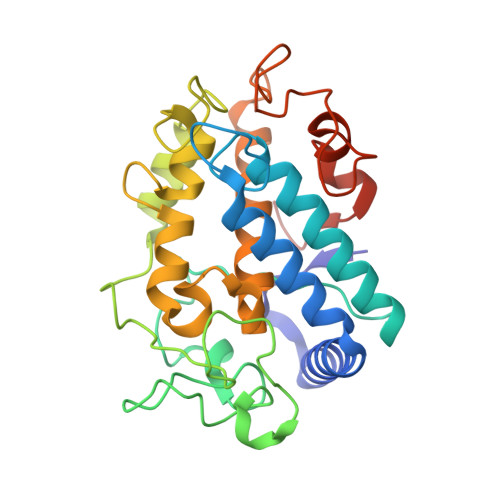
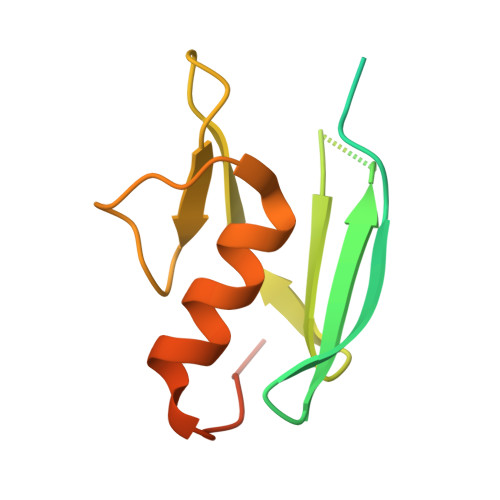
At high resolution, we determined the crystal structures of copper-bound and metal-free tyrosinase in a complex with ORF378 designated as a "caddie" protein because it assists with transportation of two CuII ions into the tyrosinase catalytic center. These structures suggest that the caddie protein covers the hydrophobic molecular surface of tyrosinase and interferes with the binding of a substrate tyrosine to the catalytic site of tyrosinase. The caddie protein, which consists of one six-strandedbeta-sheet and one alpha-helix, has no similarity with all proteins deposited into the Protein Data Bank. Although tyrosinase and catechol oxidase are classified into the type 3 copper protein family, the latter enzyme lacks monooxygenase activity. The difference in catalytic activity is based on the structural observations that a large vacant space is present just above the active center of tyrosinase and that one of the six His ligands for the two copper ions is highly flexible. These structural characteristics of tyrosinase suggest that, in the reaction that catalyzes the ortho-hydroxylation of monophenol, one of the two Cu(II) ions is coordinated by the peroxide-originated oxygen bound to the substrate. Our crystallographic study shows evidence that the tyrosinase active center formed by dinuclear coppers is flexible during catalysis.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Microbiology and Biotechnology, Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, Hiroshima University, Hiroshima, Japan.