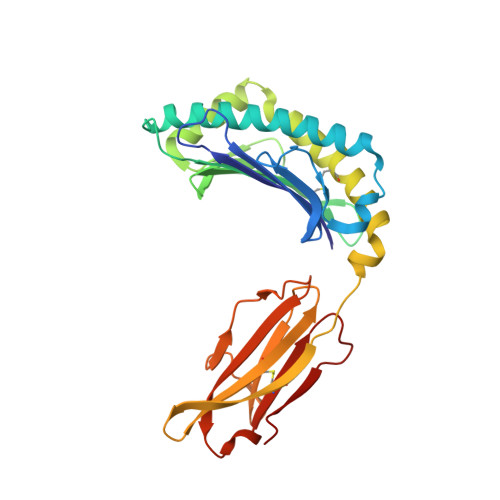
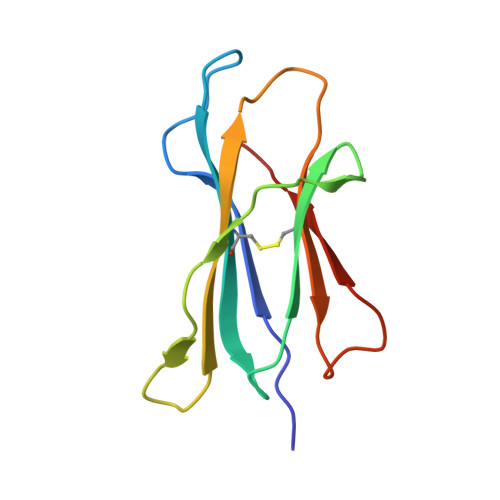
Crystal Structures of Murine Mhc Class I H-2 D(B) and K(B) Molecules in Complex with Ctl Epitopes from Influenza a Virus: Implications for Tcr Repertoire Selection and Immunodominance
Meijers, R., Lai, C., Yang, Y., Liu, J., Zhong, W., Wang, J., Reinherz, E.L.(2005) J Mol Biol 345: 1099
- PubMed: 15644207
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.11.023
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1WBX, 1WBY, 1WBZ - PubMed Abstract:
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) responses against influenza A virus in C57BL/6 mice are dominated by a small number of viral peptides among many that are capable of binding to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules. The basis of this limited immune recognition is unknown. Here, we present X-ray structures of MHC class I molecules in complex with two immunodominant epitopes (PA(224-233)/D(b) and PB1(703-711)/K(b)) and one non-immunogenic epitope (HA(468-477)/D(b)) of the influenza A virus. The immunodominant peptides are each characterized by a bulge at the C terminus, lifting P6 and P7 residues out of the MHC groove, presenting featured structural elements to T-cell receptors (TCRs). Immune recognition of PA(224-233)/D(b) will focus largely on the exposed P7 arginine residue. In contrast, the non-immunogenic HA(468-477) peptide lacks prominent features in this C-terminal bulge. In the K(b)-bound PB1(703-711) epitope, the bulge results from a non-canonical binding motif, such that the mode of presentation of this peptide strongly resembles that of D(b)-bound peptides. Given that PA(224-233)/D(b), PB1(703-711)/K(b) and the previously defined NP(366-374)/D(b) epitopes dominate the primary response to influenza A virus in C57BL/6 mice, our findings indicate that residues of the C-terminal bulge are important in selection of the immunodominant CTL repertoire.
Organizational Affiliation:
Laboratory of Immunobiology, Department of Medical Oncology, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02115, USA.