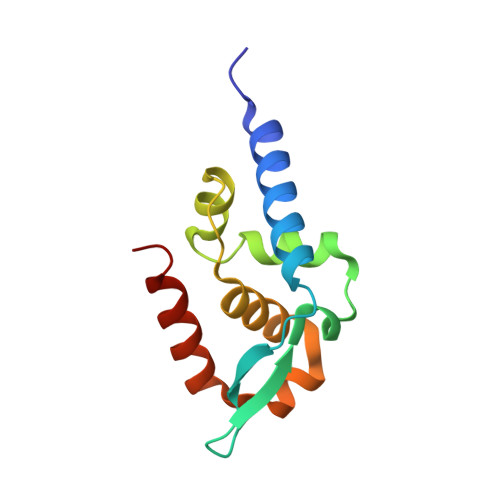
Structure and Function of the C-Terminal Domain of the Polymerase Cofactor of Rabies Virus
Mavrakis, M., Mccarthy, A.A., Roche, S., Blondel, D., Ruigrok, R.W.H.(2004) J Mol Biol 343: 819
- PubMed: 15476803
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2004.08.071
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1VYI - PubMed Abstract:
The phosphoprotein (P) of rabies virus binds the viral polymerase to the nucleoprotein (N)-RNA template for transcription and replication. By limited protease digestion we defined a monomeric C-terminal domain of P that can bind to N-RNA. The atomic structure of this domain was determined and previously described mutations that interfere with binding of P to N-RNA could now be interpreted. There appears to be two features involved in this activity situated at opposite surfaces of the molecule: a positively charged patch and a hydrophobic pocket with an exposed tryptophan side-chain. Other previously published work suggests a conformational change in P when it binds to N-RNA, which may imply the repositioning of two helices that would expose a hydrophobic groove for interaction with N. This domain of rabies virus P is structurally unrelated to the N-RNA binding domains of the phosphoproteins of Sendai and measles virus that are members of the same order of viruses, the non-segmented negative strand RNA viruses. The implications of this finding for the evolution of this virus group are discussed.
Organizational Affiliation:
EMBL Grenoble Outstation, BP181, 38042 Grenoble Cedex 9, France.