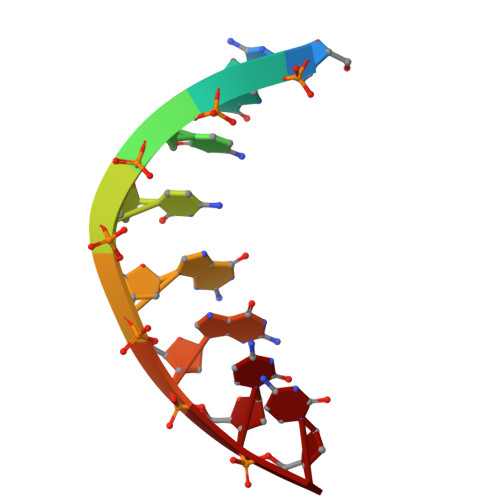
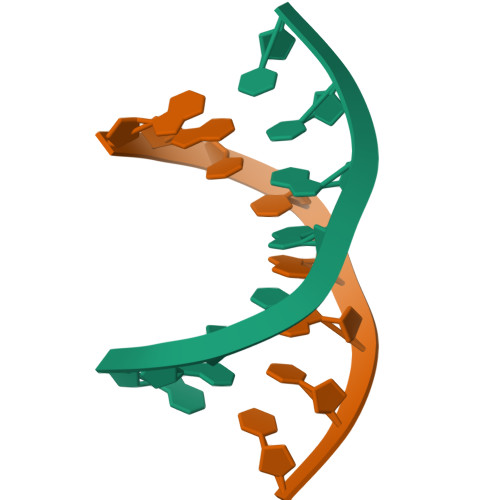
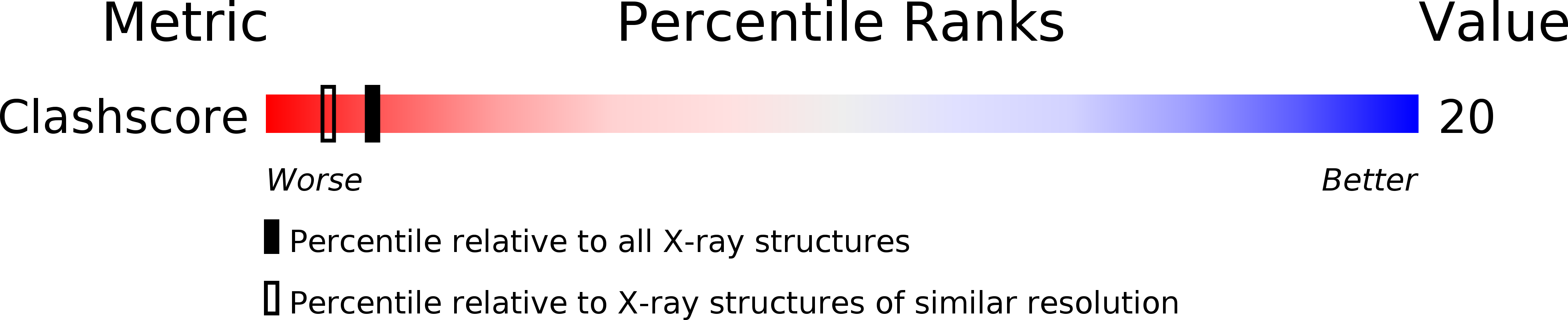Molecular structure of the octamer d(G-G-C-C-G-G-C-C): modified A-DNA.
Wang, A.H., Fujii, S., van Boom, J.H., Rich, A.(1982) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 79: 3968-3972
- PubMed: 6955784
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.79.13.3968
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1VT6 - PubMed Abstract:
The deoxynucleotide fragment d(GpGpCpCpGpGpCpC) was synthesized and crystallized, and its three-dimensional structure was determined by x-ray diffraction techniques to a resolution of 2.25 A. The molecule forms a right-handed double helix in which the two base pairs at either end of the molecule are in the conventional A-DNA conformation, while the central four base pairs have a modified form in which alternate residues have sugar conformations that are closer to those in B-DNA than in A-DNA. The molecules have an intermolecular contact in which the planar terminal guanine . cytosine base pair lies on the flat minor groove surface of the A-DNA helix.