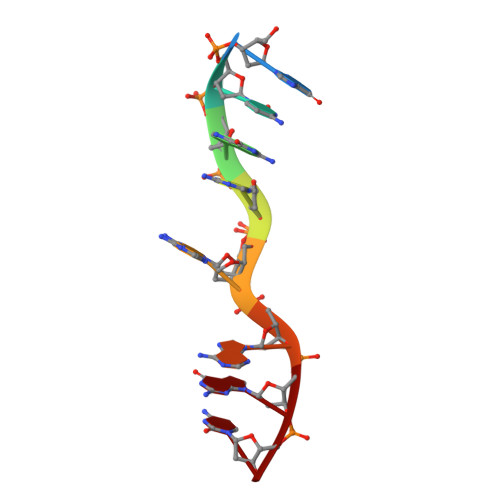
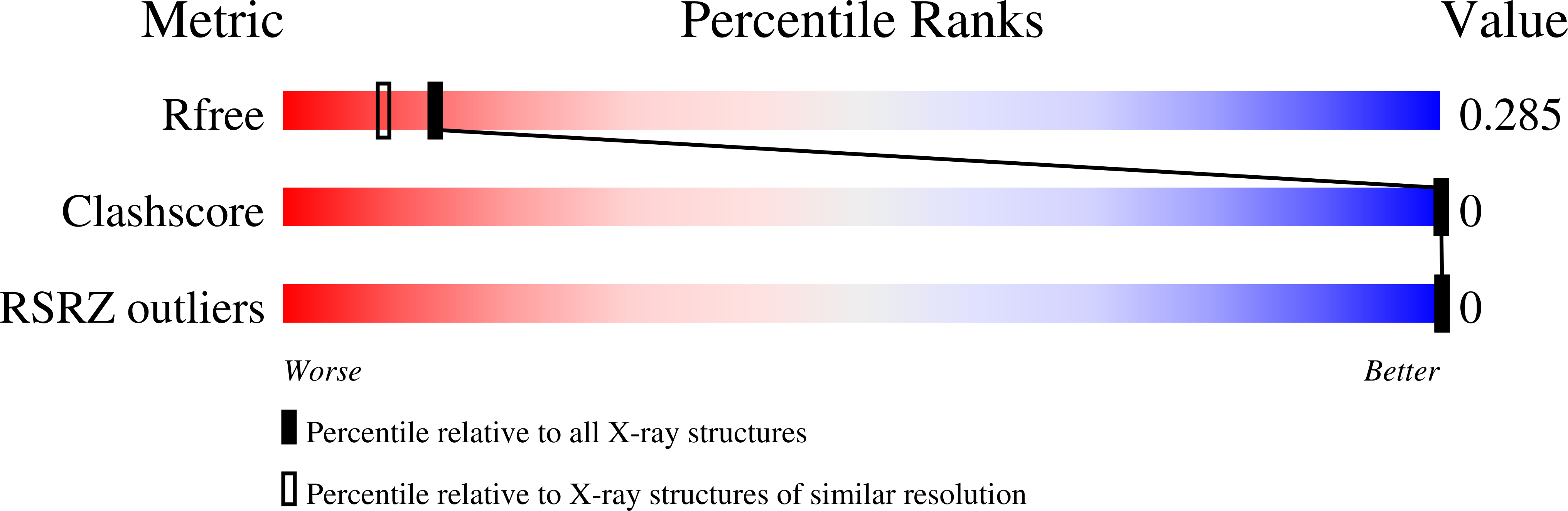Structure of d(GCGAAAGC) (hexagonal form): a base-intercalated duplex as a stable structure.
Sunami, T., Kondo, J., Hirao, I., Watanabe, K., Miura, K.I., Takenaka, A.(2004) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 60: 90-96
- PubMed: 14684897
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444903024703
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1UE2, 1UE3 - PubMed Abstract:
A DNA fragment d(GCGAAAGC), postulated to adopt a stable mini-hairpin structure on the basis of its extraordinary properties, has been X-ray analyzed. Two octamers related by a crystallographic twofold symmetry are aligned in an antiparallel fashion and associate to form a duplex, which is maintained by two Watson-Crick G.C base pairs and a subsequent sheared G.A pair at both ends. The central two A residues are free from base-pair formation. The corresponding base moieties of the two strands are intercalated and stacked on each other, forming a long column of G(1)-C(2)-G(3)-A(4)-A(5)(*)-A(5)-A(4)(*)-G(3)(*)-C(2)(*)-G(1)(*) (asterisks indicate the counter-strand). The Watson-Crick and major-groove sites of the four stacked adenine bases are exposed to the solvent region, suggesting a functional role. Since this structural motif is similar to those found in the nonamers d(G(Br)CGAAAGCT) and d(G(I)CGAAAGCT), the base-intercalated duplex may be a stable form of the specific sequence. Electrophoresis results suggest that the octamer has two states, monomeric and dimeric, in solution depending on the Mg(2+) concentration. The present duplex is preferred under the crystallization conditions, which correspond to physiologically allowed conditions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Graduate School of Bioscience and Biotechnology, Tokyo Institute of Technology, Yokohama 226-8501, Japan.