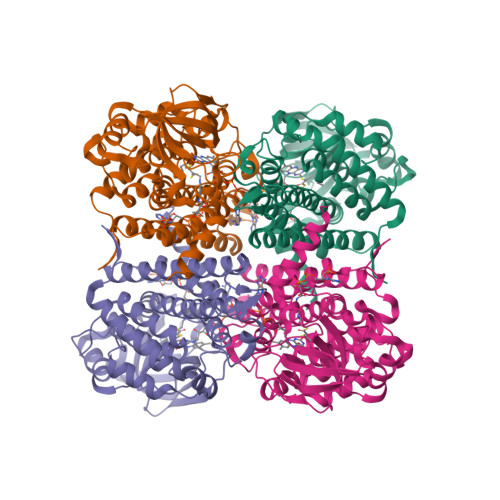
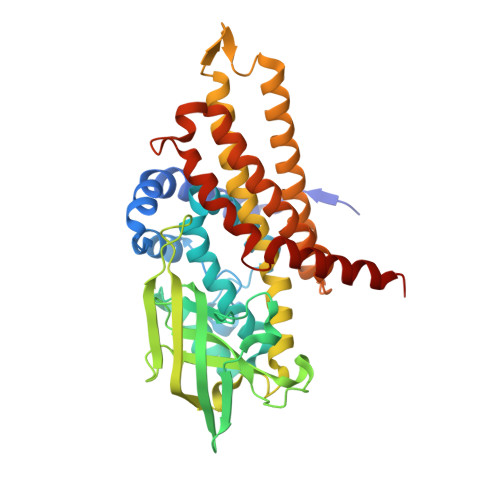
Structure of the transition state analog of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Crystallographic and molecular orbital studies on the charge-transfer complex of medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase with 3-thiaoctanoyl-CoA
Satoh, A., Nakajima, Y., Miyahara, I., Hirotsu, K., Tanaka, T., Nishina, Y., Shiga, K., Tamaoki, H., Setoyama, C., Miura, R.(2003) J Biochem 134: 297-304
- PubMed: 12966080
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvg143
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1UDY - PubMed Abstract:
The flavoenzyme medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD) eliminates the alpha-proton of the substrate analog, 3-thiaoctanoyl-CoA (3S-C8-CoA), to form a charge-transfer complex with deprotonated 3S-C8-CoA. This complex can simulate the metastable reaction intermediate immediately after the alpha-proton elimination of a substrate and before the beta-hydrogen transfer as a hydride, and is therefore regarded as a transition-state analog. The crystalline complex was obtained by co-crystallizing MCAD in the oxidized form with 3S-C8-CoA. The three-dimensional structure of the complex was solved by X-ray crystallography. The deprotonated 3S-C8-CoA was clearly located within the active-site cleft of the enzyme. The arrangement between the flavin ring and deprotonated 3S-C8-CoA is consistent with a charge transfer interaction with the negatively charged acyl-chain of 3S-C8-CoA as an electron donor stacking on the pyrimidine moiety of the flavin ring as an electron acceptor. The structure of the model complex between lumiflavin and the deprotonated ethylthioester of 3-thiabutanoic acid was optimized by molecular orbital calculations. The obtained theoretical structure was essentially the same as that of the corresponding region of the X-ray structure. A considerable amount of negative charge is transferred to the flavin ring system to stabilize the complex by 9.2 kcal/mol. The large stabilization energy by charge transfer probably plays an important role in determining the alignment of the flavin ring with 3S-C8-CoA. The structure of the highest occupied molecular orbital of the complex revealed the electron flow pathway from a substrate to the flavin ring.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, Osaka City University, Sumiyoshi-ku, Osaka 558-8585.