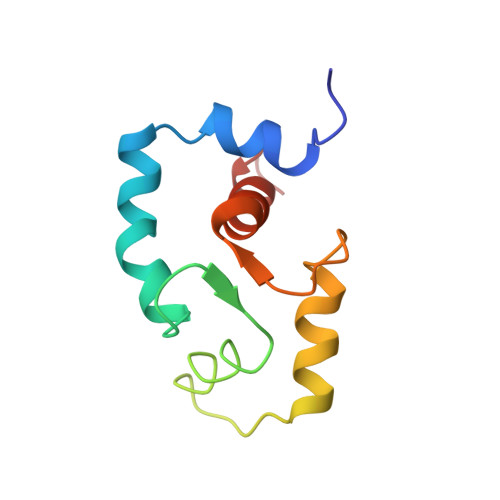
Structures of the troponin C regulatory domains in the apo and calcium-saturated states.
Gagne, S.M., Tsuda, S., Li, M.X., Smillie, L.B., Sykes, B.D.(1995) Nat Struct Biol 2: 784-789
- PubMed: 7552750
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nsb0995-784
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TNP, 1TNQ - PubMed Abstract:
Regulation of contraction in skeletal muscle occurs through calcium binding to the protein troponin C. The solution structures of the regulatory domain of apo and calcium-loaded troponin C have been determined by multinuclear, multidimensional nuclear magnetic resonance techniques. The structural transition in the regulatory domain of troponin C on calcium binding involves an opening of the structure through large changes in interhelical angles. This leads to the increased exposure of an extensive hydrophobic patch, an event that triggers skeletal muscle contraction.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada.