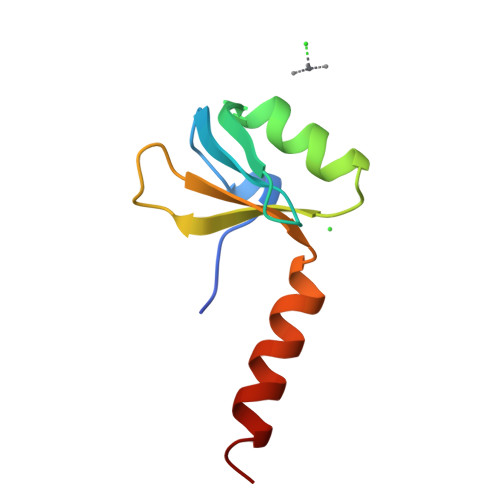
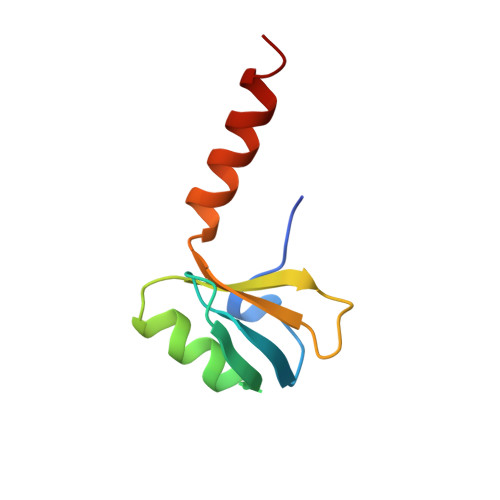
X-ray crystallography shows that translational initiation factor IF3 consists of two compact alpha/beta domains linked by an alpha-helix.
Biou, V., Shu, F., Ramakrishnan, V.(1995) EMBO J 14: 4056-4064
- PubMed: 7664745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00077.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1TIF, 1TIG - PubMed Abstract:
The structures of the two domains of translational initiation factor IF3 from Bacillus stearothermophilus have been solved by X-ray crystallography using single wavelength anomalous scattering and multiwavelength anomalous diffraction. Each of the two domains has an alpha/beta topology, with an exposed beta-sheet that is reminiscent of several ribosomal and other RNA binding proteins. An alpha-helix that protrudes out from the body of the N-terminal domain towards the C-terminal domain suggests that IF3 consists of two RNA binding domains connected by an alpha-helix and that it may bridge two regions of the ribosome. This represents the first high resolution structural information on a translational initiation factor.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biology Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory, Upton, NY 11973, USA.