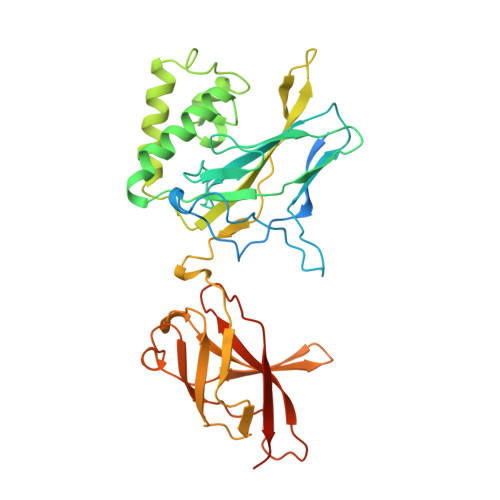
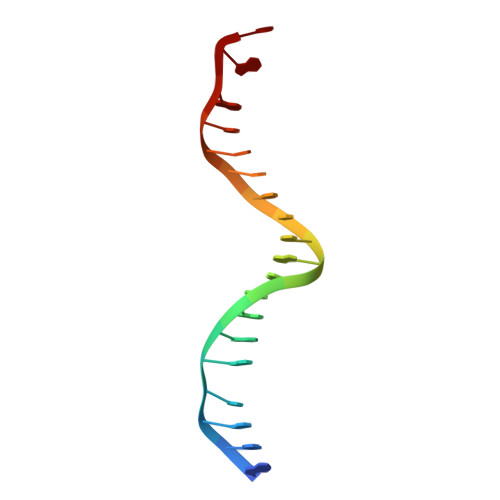
Structure of the NF-kappa B p50 homodimer bound to DNA.
Muller, C.W., Rey, F.A., Sodeoka, M., Verdine, G.L., Harrison, S.C.(1995) Nature 373: 311-317
- PubMed: 7830764
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373311a0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1SVC - PubMed Abstract:
The structure of a large fragment of the p50 subunit of the human transcription factor NF-kappa B, bound as a homodimer to DNA, reveals that the Rel-homology region has two beta-barrel domains that grip DNA in the major groove. Both domains contact the DNA backbone. The amino-terminal specificity domain contains a recognition loop that interacts with DNA bases; the carboxy-terminal dimerization domain bears the site of I-kappa B interaction. The folds of these domains are related to immunoglobulin-like modules. The amino-terminal domain also resembles the core domain of p53.
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02138.
Organizational Affiliation: