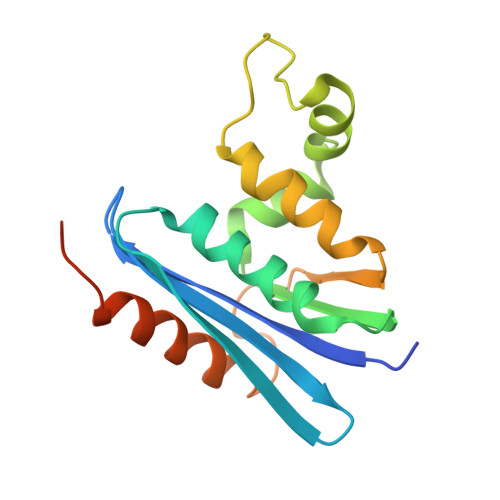
Crystal structure of ribonuclease H from Thermus thermophilus HB8 refined at 2.8 A resolution.
Ishikawa, K., Okumura, M., Katayanagi, K., Kimura, S., Kanaya, S., Nakamura, H., Morikawa, K.(1993) J Mol Biol 230: 529-542
- PubMed: 8385228
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1993.1169
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1RIL - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of Thermus thermophilus RNase H was determined at 2.8 A resolution. The structure was solved by the molecular replacement method, based on the accurately refined structure of Escherichia coli RNase HI, which shows 52% amino acid sequence identity. Crystallographic refinement led to an R-factor of 0.205, with a 0.019 A root-mean-square deviation from ideal bond lengths and 0.048 A from ideal bond angle distances. Structural comparison shows a striking similarity in the overall folding of the thermophilic and mesophilic enzymes. The root-mean-square displacement is 0.95 A between equivalent alpha-carbon atoms from all elements of secondary structure (five alpha-helices and five beta-strands). However, some notable differences, which account for the enhanced thermostability of T. thermophilus RNase H, are observed in loop structures and side-chain conformations. The substitution of Gly for the left-handed helical residue (Lys95) in the E. coli enzyme is proposed to substantially enhance the thermostability, due to the release of steric hindrance caused by the beta-carbon atom. Furthermore, it is likely that the expansion of an aromatic cluster, arising from the replacement of Ile78 in the mesophilic enzyme by Phe, and the increased number of salt-bridges additively contribute to the stability.
Organizational Affiliation:
Protein Engineering Research Institute, Osaka, Japan.