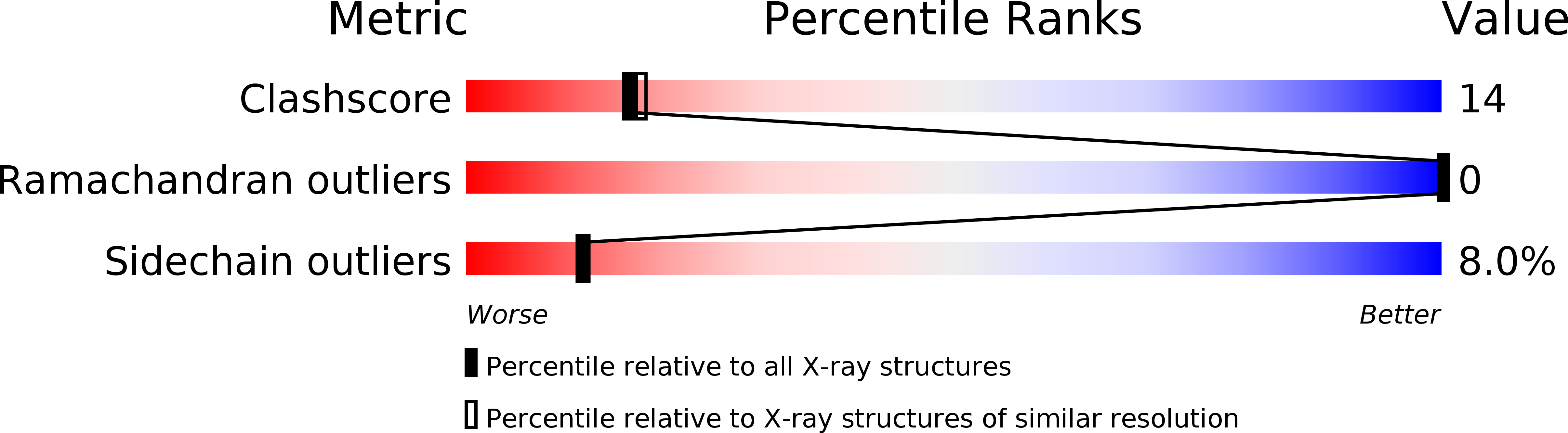Crystal structure of the post-chaperonin beta-tubulin binding cofactor Rbl2p
Steinbacher, S.(1999) Nat Struct Biol 6: 1029-1032
- PubMed: 10542094
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/14912
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1QSD - PubMed Abstract:
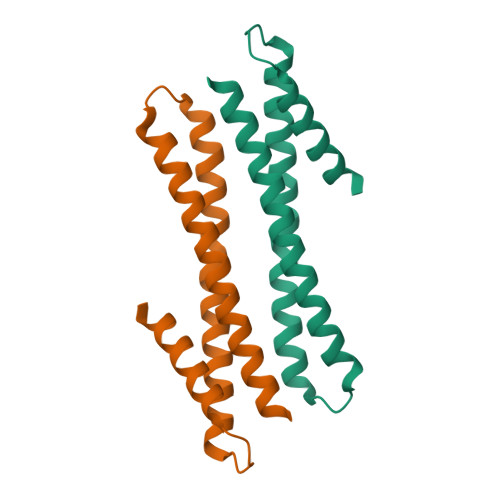
The folding pathway of tubulins includes highly specific interactions with a series of cofactors (A, B, C, D and E) after they are released from the eukaryotic chaperonin CCT. The 2.2 A crystal structure of Rbl2p, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae homolog of beta-tubulin specific cofactor A, shows alpha-helical monomers forming a flat, slightly convex dimer. The surface of the molecule is dominated by polar and charged residues and lacks hydrophobic patches typically observed for chaperones that bind unfolded or partially folded proteins. This post-chaperonin cofactor is therefore clearly distinct from typical chaperones where hydrophobicity is a hallmark of substrate recognition.
Organizational Affiliation:
Max-Planck-Institut für Biochemie, Abteilung Strukturforschung, Am Klopferspitz 18a, 82152 Martinsried, Germany.