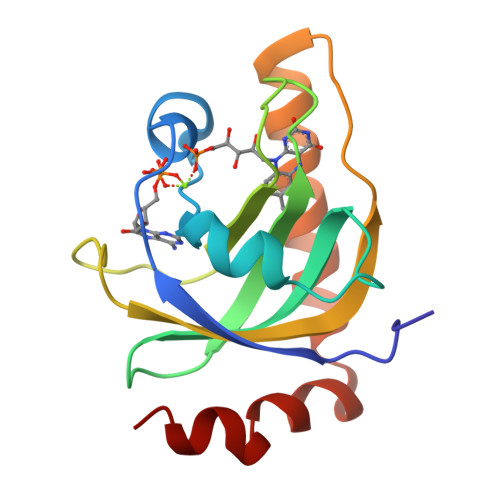
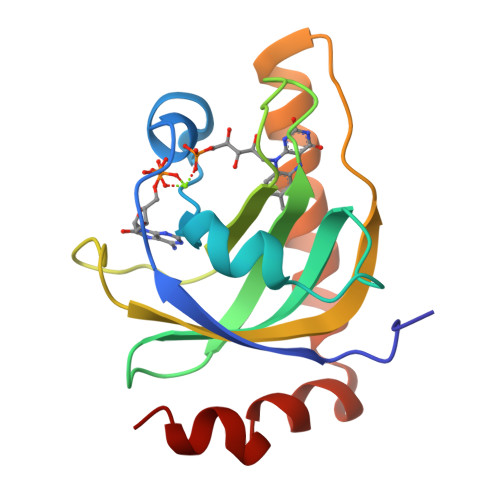
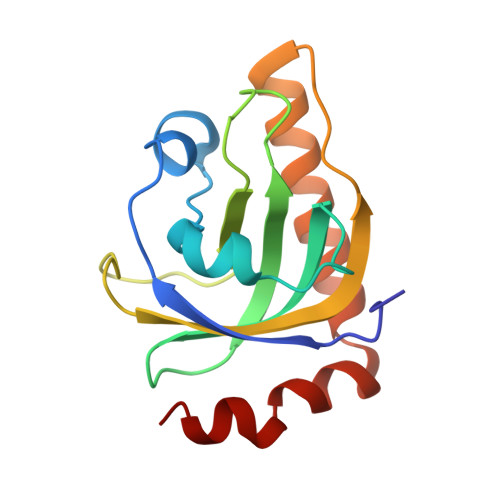
Ligand binding-induced conformational changes in riboflavin kinase: structural basis for the ordered mechanism.
Karthikeyan, S., Zhou, Q., Osterman, A.L., Zhang, H.(2003) Biochemistry 42: 12532-12538
- PubMed: 14580199
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi035450t
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1Q9S - PubMed Abstract:
Riboflavin kinase (RFK) is an essential enzyme catalyzing the phosphorylation of riboflavin (vitamin B(2)) in the presence of ATP and Mg(2+) to form the active cofactor FMN, which can be further converted to FAD. Previously, the crystal structures of RFKs from human and Schizosaccharomyces pombe have been determined in the apo form and in complex with MgADP. These structures revealed that RFK adopts a novel kinase fold and utilizes a unique nucleotide binding site. The structures of the flavin-bound RFK obtained by soaking pre-existing crystals were also reported. Because of crystal packing restraints, these flavin-bound RFK complexes adopt conformations nearly identical with that of corresponding flavin-free structures. Here we report the structure of human RFK cocrystallized with both MgADP and FMN. Drastic conformational changes associated with flavin binding are observed primarily at the so-called Flap I and Flap II loop regions. As a result, the bound FMN molecule now interacts with the enzyme extensively and is well-ordered. Residues from Flap II interact with Flap I and shield the FMN molecule from the solvent. The conformational changes in Flap I resulted in a new Mg(2+) coordination pattern in which a FMN phosphate oxygen and Asn36 side chain carbonyl are directly coordinating to the Mg(2+) ion. The proposed catalytic base Glu86 is well-positioned for activation of the O5' hydroxyl group of riboflavin for the phosphoryl transfer reaction. The structural data obtained so far on human and yeast RFK complexes provide a rationale for the ordered kinetic mechanism of RFK.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, Texas 75390, USA.