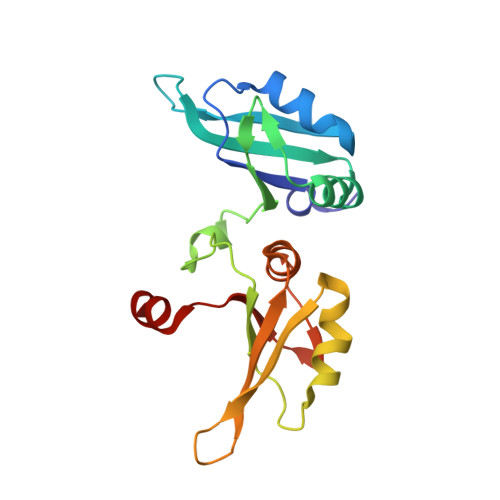
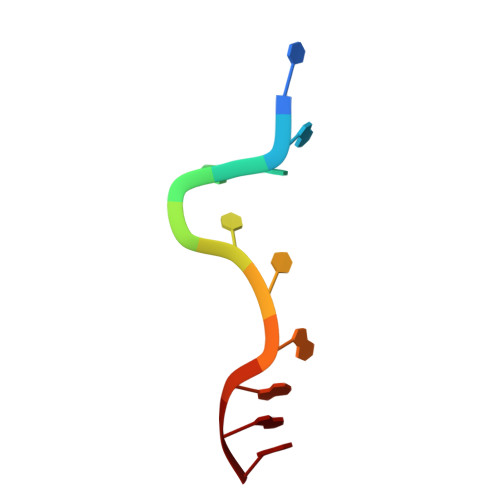
Structure-based incorporation of 6-methyl-8-(2-deoxy-beta-ribofuranosyl)isoxanthopteridine into the human telomeric repeat DNA as a probe for UP1 binding and destabilization of G-tetrad structures
Myers, J.C., Moore, S.A., Shamoo, Y.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 42300-42306
- PubMed: 12904298
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M306147200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PGZ, 1PO6 - PubMed Abstract:
Heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNP A1) is an abundant nuclear protein that participates in RNA processing, alternative splicing, and chromosome maintenance. hnRNP A1 can be proteolyzed to unwinding protein (UP1), a 22.1-kDa protein that retains a high affinity for purine-rich single-stranded nucleic acids, including the human telomeric repeat (hTR) d(TTAGGG)n. Using the structure of UP1 bound to hTR as a guide, we have incorporated the fluorescent guanine analog 6-MI at one of two positions within the DNA to facilitate binding studies. One is where 6-MI remains stacked with an adjacent purine, and another is where it becomes fully unstacked upon UP1 binding. The structures of both modified oligonucleotides complexed to UP1 were determined by x-ray crystallography to validate the efficacy of our design, and 6-MI has proven to be an excellent reporter molecule for single-stranded nucleic acid interactions in positions where there is a change in stacking environment upon complex formation. We have shown that UP1 affinity for d(TTAGGG)2 is approximately 5 nm at 100 mm NaCl, pH 6.0, and our binding studies with d(TTAGG(6-MI)TTAGGG) show that binding is only modestly sensitive to salt and pH. UP1 also has a potent G-tetrad destabilizing activity that reduces the Tm of the hTR sequence d(TAGGGT)4 from 67.0 degrees C to 36.1 degrees C at physiological conditions (150 mm KCl, pH 7.0). Consistent with the structures determined by x-ray crystallography, UP1 is able to bind the hTR sequence in solution as a dimer and supports a model for hnRNP A1 binding to nucleic acids in arrays that may make a contiguous set of anti-parallel single-stranded nucleic acid binding clefts. These data suggest that seemingly disparate roles for hnRNP A1 in alternative splice site selection, RNA processing, RNA transport, and chromosome maintenance reflect its ability to bind a purine-rich consensus sequence (nYAGGn) and destabilize potentially deleterious G-tetrad structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Rice University, 6100 S. Main Street, Houston, TX 77005, USA.