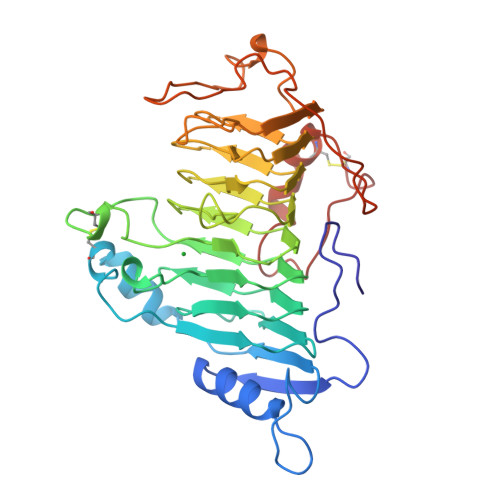
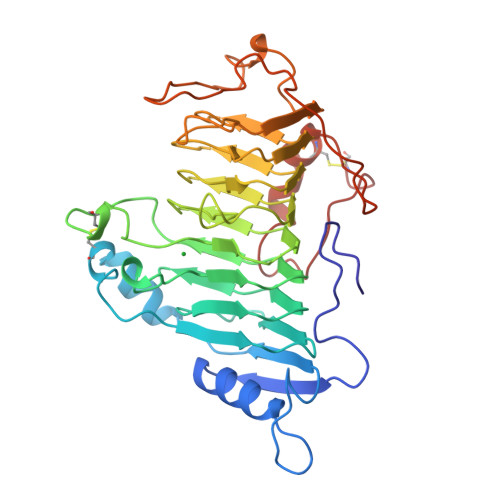
The Refined Three-Dimensional Structure of Pectate Lyase C from Erwinia chrysanthemi at 2.2 Angstrom Resolution (Implications for an Enzymatic Mechanism).
Yoder, M.D., Jurnak, F.(1995) Plant Physiol 107: 349-364
- PubMed: 12228363
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.2.349
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PLU - PubMed Abstract:
The crystal structure of pectate lyase C (EC 4.2.2.2) from the enterobacterium Erwinia chrysanthemi (PelC) has been refined by molecular dynamics techniques to a resolution of 2.2 A to an R factor of 17.97%. The final model consists of 352 of the total 353 amino acids and 114 solvent molecules. The root-mean-square deviation from ideality is 0.009 A for bond lengths and 1.768[deg] for bond angles. The structure of PelC bound to the lanthanide ion lutetium, used as a calcium analog, has also been refined. Lutetium inhibits the enzymatic activity of the protein, and in the PelC-lutetium structure, the ion binds in the putative calcium-binding site. Five side-chain atoms form ligands to the lutetium ion. An analysis of the atomic-level model of the two protein structures reveals possible implications for the enzymatic mechanism of the enzyme.
Organizational Affiliation:
School of Biological Sciences, Division of Cell Biology and Biophysics, University of Missouri, Kansas City, Missouri 64110 (M.D.Y.).