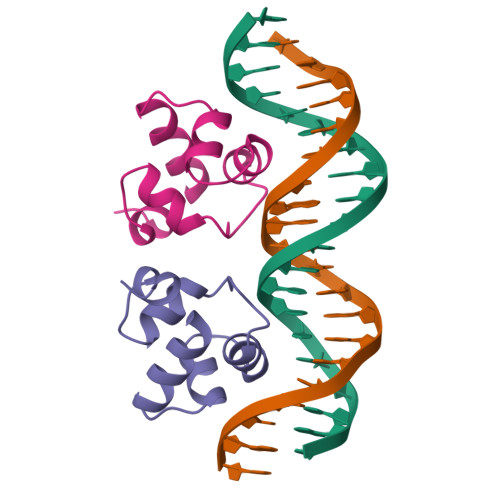
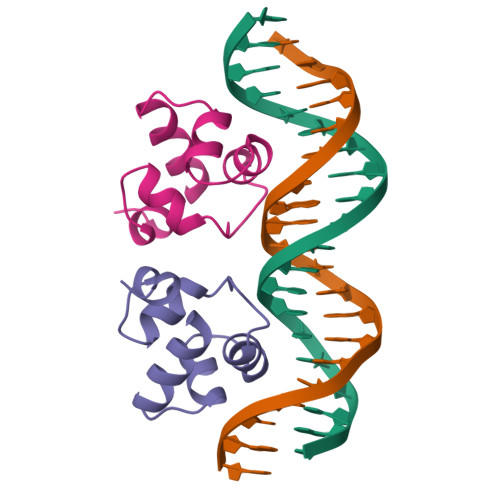
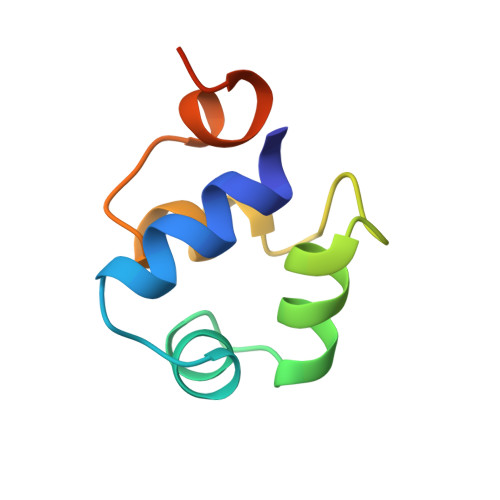
The complex between phage 434 repressor DNA-binding domain and operator site OR3: structural differences between consensus and non-consensus half-sites.
Rodgers, D.W., Harrison, S.C.(1993) Structure 1: 227-240
- PubMed: 8081737
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0969-2126(93)90012-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1PER - PubMed Abstract:
The repressor of phage 434 binds to a set of operator sites as a homodimer. Its relative affinities for these sites determine the switch from lysogenic to lytic growth. The six 434 operator sites (OR1, OR2, OR3, OL1, OL2 and OL3) have a particularly simple organization; all are 14 base pairs long, with a conserved 5'-ACAA sequence symmetrically placed at either end, and a variable central six base pairs. OR3 is unique among naturally-occurring 434 operator sites in that it contains a non-consensus base pair, G.C, at the fourth position of the otherwise invariant 5'-ACAA sequence. Comparisons among structures of the 434 repressor DNA-binding domain, R1-69, bound to various operator sites, allow us to analyze differential specificity in regulatory complexes of this kind. We have determined the structure at 2.5 A resolution of a complex of R1-69 with DNA containing the OR3 site and compared it with previously studied complexes of R1-69 bound to OR1 and OR2. There are surprisingly extensive structural differences between the consensus and non-consensus half-sites of OR3 with respect to their interactions with R1-69, including a shift in the DNA backbone and a small rotation of the entire R1-69 monomer. Recognition of the base pair difference that is critical for the 434 regulatory switch involves a number of amino acid residues, not just the one or two side chains in direct contact with the G-C base pair. Moreover, the repressor imposes a somewhat altered DNA conformation on the non-consensus half-site.
Organizational Affiliation:
Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA 02138.