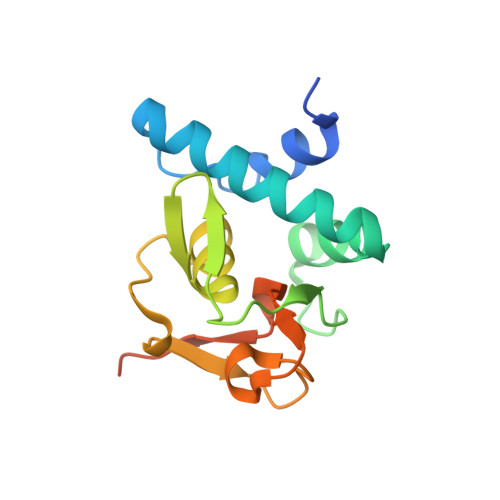
Features of a Smad3 MH1-DNA complex. Roles of water and zinc in DNA binding.
Chai, J., Wu, J.-W., Yan, N., Massague, J., Pavletich, N.P., Shi, Y.(2003) J Biol Chem 278: 20327-20331
- PubMed: 12686552
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C300134200
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OZJ - PubMed Abstract:
The Smad family of proteins mediates transforming growth factor-beta signaling from cell membrane to the nucleus. In the nucleus, Smads serve as transcription factors by directly binding to specific DNA sequences and regulating the expression of ligand-response genes. A previous structural analysis, at 2.8-A resolution, revealed a novel DNA-binding mode for the Smad MH1 domain but did not allow accurate assignment of the fines features of protein-DNA interactions. The crystal structure of a Smad3 MH1 domain bound to a palindromic DNA sequence, determined at 2.4-A resolution, reveals a surprisingly important role for water molecules. The asymmetric placement of the DNA-binding motif (a conserved 11-residue beta-hairpin) in the major groove of DNA is buttressed by seven well ordered water molecules. These water molecules make specific hydrogen bonds to the DNA bases, the DNA phosphate backbones, and several critical Smad3 residues. In addition, the MH1 domain is found to contain a bound zinc atom using four invariant residues among Smad proteins, three cysteines and one histidine. Removal of the zinc atom results in compromised DNA binding activity. These results define the Smad MH1 domain as a zinc-coordinating module that exhibits unique DNA binding properties.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology, Princeton University, Lewis Thomas Laboratory, New Jersey 08544, USA.