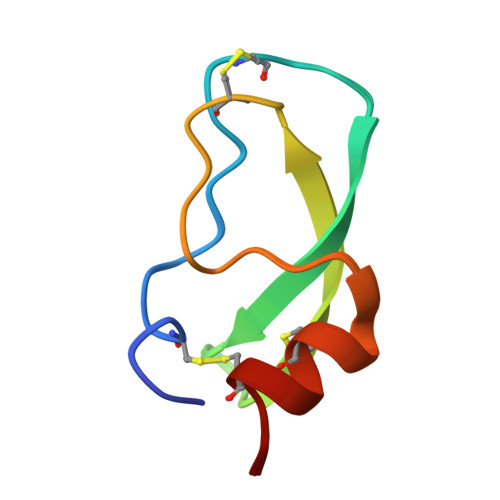
The Solution Structure of Bovine Pancreatic Trypsin Inhibitor at High Pressure
Williamson, M.P., Akasaka, K., Refaee, M.(2003) Protein Sci 12: 1971
- PubMed: 12930996
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1110/ps.0242103
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1OA5, 1OA6 - PubMed Abstract:
The solution structure of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) at a pressure of 2 kbar is presented. The structure was calculated as a change from an energy-minimized low-pressure structure, using (1)H chemical shifts as restraints. The structure has changed by 0.24 A RMS, and has almost unchanged volume. The largest changes as a result of pressure are in the loop 10-16, which contains the active site of BPTI, and residues 38-42, which are adjacent to buried water molecules. Hydrogen bonds are compressed by 0.029 +/- 0.117 A, with the longer hydrogen bonds, including those to internal buried water molecules, being compressed more. The hydrophobic core is also compressed, largely from reduction of packing defects. The parts of the structure that have the greatest change are close to buried water molecules, thus highlighting the importance of water molecules as the nucleation sites for volume fluctuation of proteins in native conditions.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, University of Sheffield, Western Bank, Sheffield S10 2TN, UK. m.williamson@sheffield.ac.uk