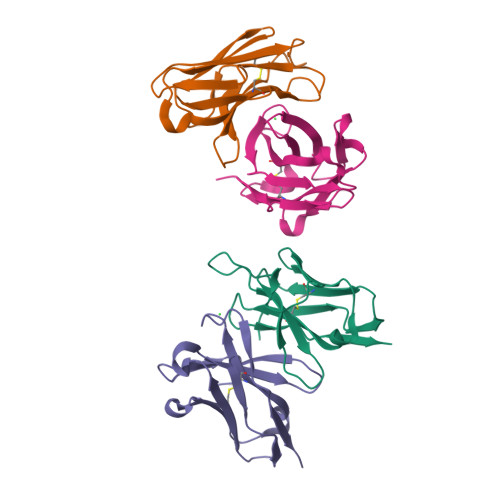
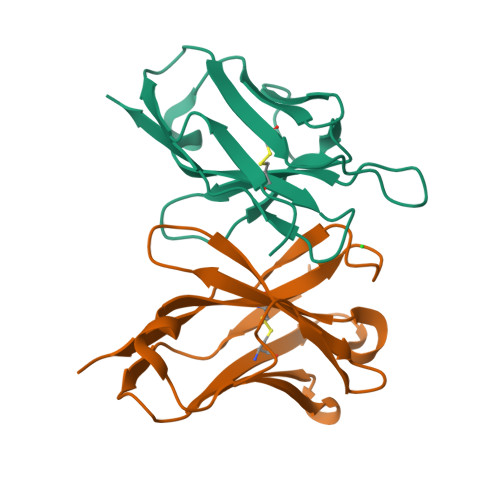
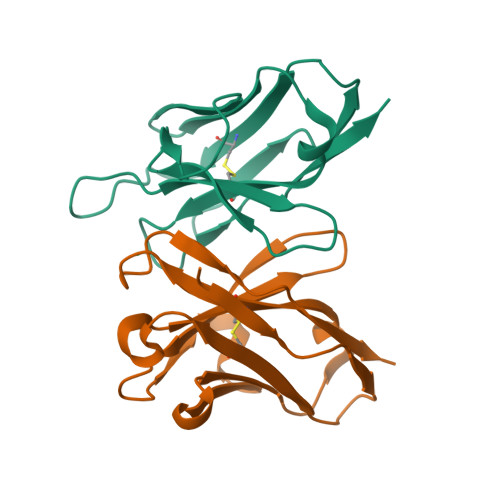
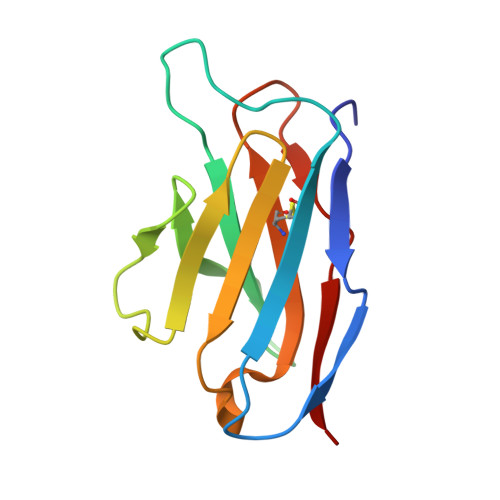
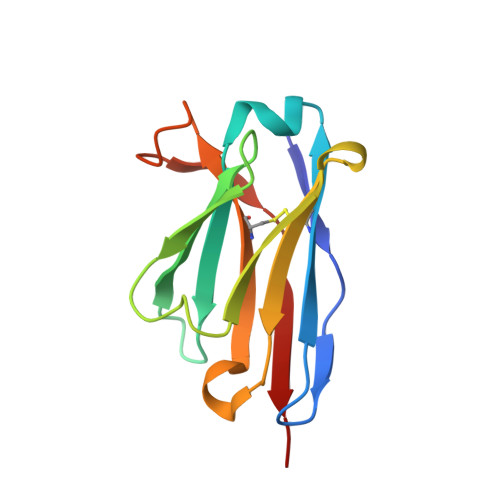
Structure of a single-chain Fv fragment of an antibody that inhibits the HIV-1 and HIV-2 proteases.
Lescar, J., Brynda, J., Fabry, M., Horejsi, M., Rezacova, P., Sedlacek, J., Bentley, G.A.(2003) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 59: 955-957
- PubMed: 12777823
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/s0907444903003597
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1N4X - PubMed Abstract:
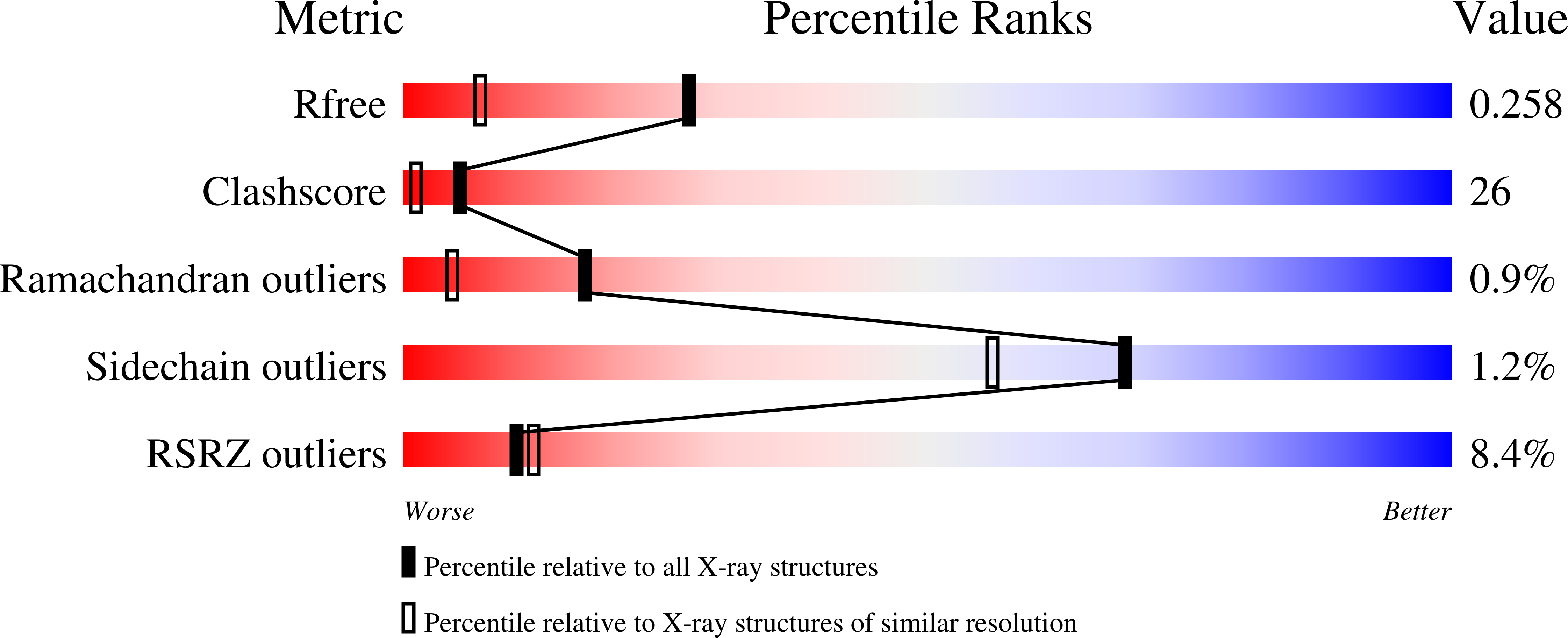
The monoclonal antibody 1696, which was raised against the HIV-1 protease, inhibits the catalytic activity of the enzyme from both the HIV-1 and HIV-2 strains. The antibody cross-reacts with peptides containing the N-terminus of the enzyme, which is highly conserved between these strains. The crystal structure of a single-chain Fv fragment of 1696 (scFv-1696) in the non-complexed form, solved at 1.7 A resolution, is compared with the previously reported non-complexed Fab-1696 and antigen-bound scFv-1696 structures. Large conformational changes in the third hypervariable region of the heavy chain and differences in relative orientation of the variable domains are observed between the different structures.
Organizational Affiliation:
European Synchrotron Radiation Facility, BP 220, F-38043 Grenoble, France.