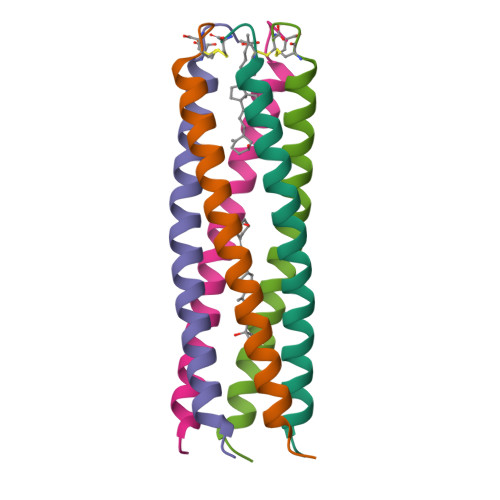
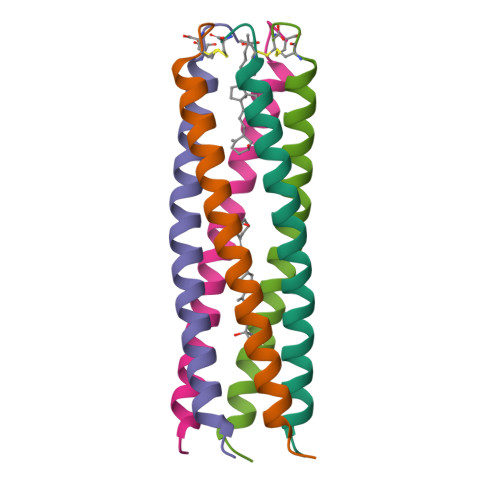
Storage function of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein: the crystal structure of the coiled-coil domain in complex with vitamin D(3).
Ozbek, S., Engel, J., Stetefeld, J.(2002) EMBO J 21: 5960-5968
- PubMed: 12426368
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdf628
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MZ9 - PubMed Abstract:
The five-stranded coiled-coil domain of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMPcc) forms a continuous axial pore with binding capacities for hydrophobic compounds, including prominent cell signalling molecules. Here, we report the X-ray structure of the COMPcc domain in complex with vitamin D(3) at 1.7 A resolution. The COMPcc pentamer harbours two molecules of the steroid hormone precursor in a planar s-trans conformation of the conjugated triene, with the aliphatic tails lying along the molecule axis. A hydrophilic ring of five Gln54 side chains divides the channel into two hydrophobic compartments in which the bound vitamin D(3) pair is fixed in a head-to-head orientation. Vitamin D(3) binding induces a volumetric increase of the cavities of approximately 30% while the main chain distances of the pentamer are retained. This adaptation to the bulky ring systems of the ligands is accomplished by a rotamer re-orientation of beta-branched side chains that form the knobs into holes of the coiled-coil structure. Compared with binding of vitamin D and retinoic acid by their classical receptors, COMP exerts a distinct mechanism of interaction mainly defined by the pattern of hydrophobic core residues.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysical Chemistry, Biozentrum, University of Basel, Klingelbergstrasse 70, CH-4056 Basel, Switzerland. Suat.Oezbek@unibas.ch