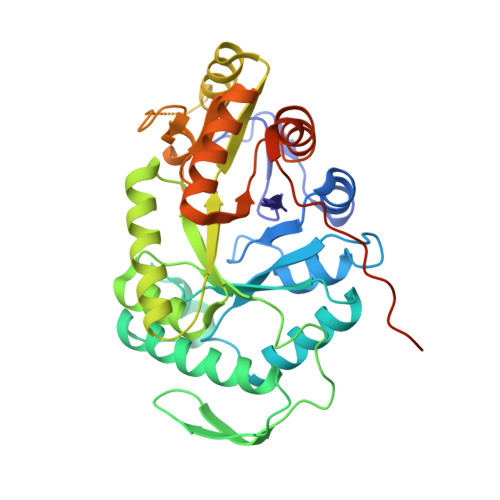
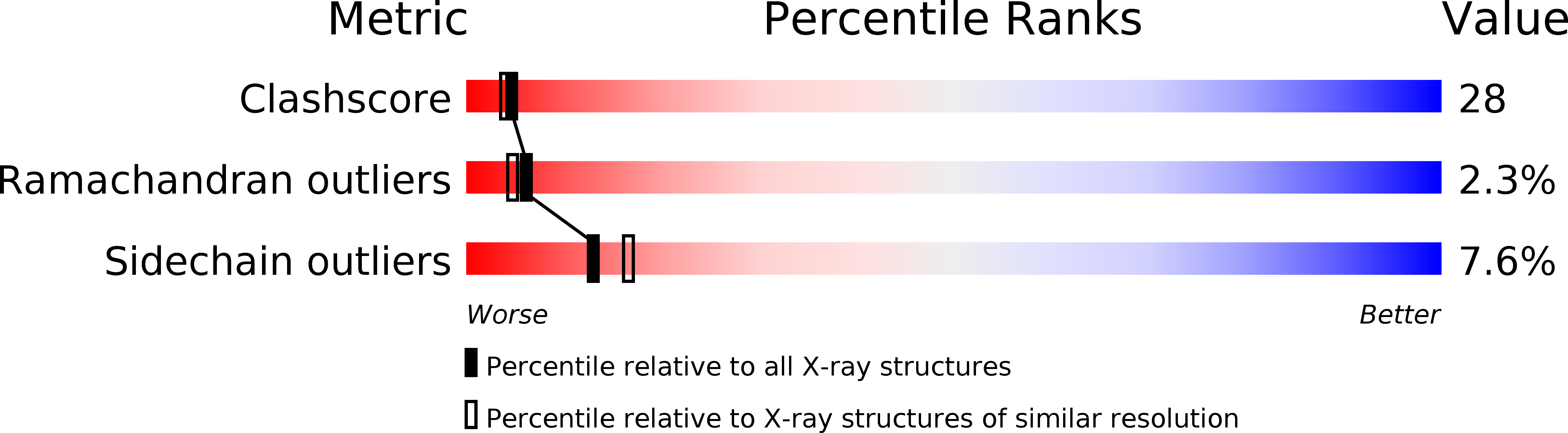Crystal Structure of Escherichia coli Alkanesulfonate Monooxygenase SsuD
Eichhorn, E., Davey, C.A., Sargent, D.F., Leisinger, T., Richmond, T.J.(2002) J Mol Biol 324: 457-468
- PubMed: 12445781
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-2836(02)01069-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1M41 - PubMed Abstract:
The FMNH(2)-dependent alkanesulfonate monooxygenase SsuD catalyzes the conversion of alkanesulfonates to the corresponding aldehyde and sulfite. The enzyme allows Escherichia coli to use a wide range of alkanesulfonates as sulfur sources for growth when sulfate or cysteine are not available. The structure of SsuD was solved using the multiwavelength anomalous dispersion method from only four ordered selenium sites per asymmetric unit (one site per 20,800 Da). The final model includes 328 of 380 amino acid residues and was refined to an R-factor of 23.5% (R(free)=27.5%) at 2.3A resolution. The X-ray crystal structure of SsuD shows a homotetrameric state for the enzyme, each subunit being composed of a TIM-barrel fold enlarged by four insertion regions that contribute to intersubunit interactions. SsuD is structurally related to a bacterial luciferase and an archaeal coenzyme F(420)-dependent reductase in spite of a low level of sequence identity with these enzymes. The structural relationship is not limited to the beta-barrel region; it includes most but not all extension regions and shows distinct properties for the SsuD TIM-barrel. A likely substrate-binding site is postulated on the basis of the SsuD structure presented here, results from earlier biochemical studies, and structure relatedness to bacterial luciferase. SsuD is related to other FMNH(2)-dependent monooxygenases that show distant sequence relationship to luciferase. Thus, the structure reported here provides a model for enzymes belonging to this family and suggests that they might all fold as TIM-barrel proteins.
Organizational Affiliation:
ETH Zürich, Institut für Molekularbiologie und Biophysik, ETH-Hönggerberg, CH-8093, Zurich, Switzerland.