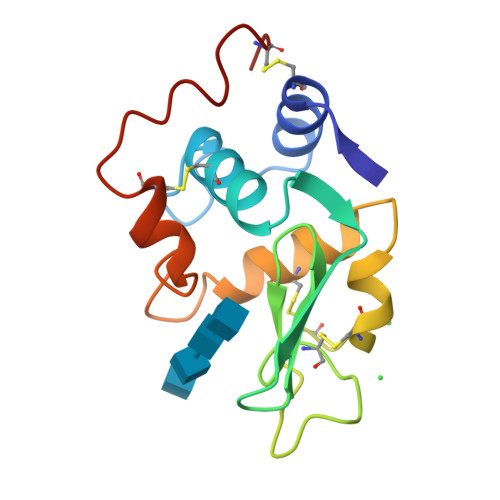
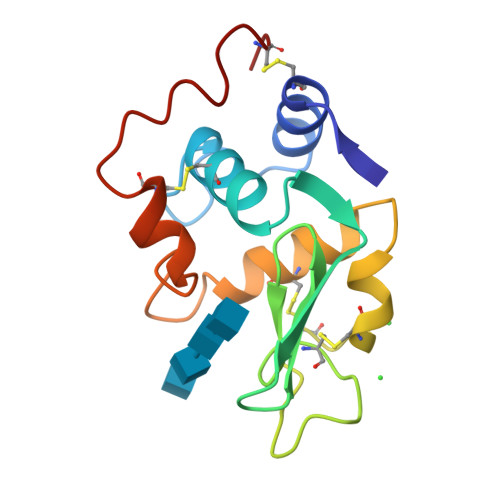
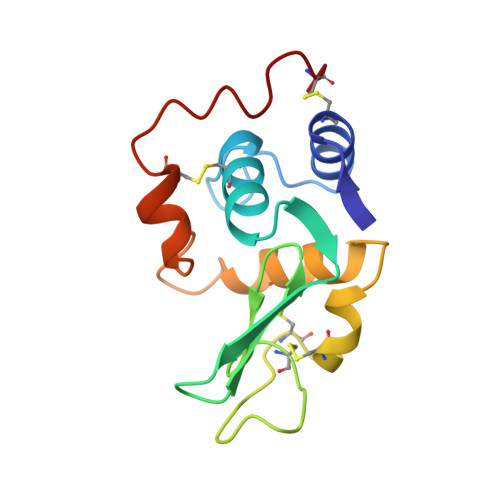
Structural changes of active site cleft and different saccharide binding modes in human lysozyme co-crystallized with hexa-N-acetyl-chitohexaose at pH 4.0.
Song, H., Inaka, K., Maenaka, K., Matsushima, M.(1994) J Mol Biology 244: 522-540
- PubMed: 7990138
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1LZR, 1LZS - PubMed Abstract:
Human lysozyme was co-crystallized with hexa-N-acetyl-chitohexaose, (GlcNAc)6, at pH 4.0 and 4.0 degrees C in a new orthorhombic form, where two protein molecules, MOL1 and MOL2, were contained in an asymmetric unit. The three-dimensional structure was refined to an R-factor of 17.0% at 1.6 A resolution. It was found that (GlcNAc)6 had already been cleaved to (GlcNAc)4 and (GlcNAc)2. In MOL1, (GlcNAc)4 was bound to the A, B, C, and D subsites, and binding sites of (GlcNAc)2 were close to the E and F subsites proposed on the basis of model building by Phillips and his colleagues. In MOL2, only the (GlcNAc)4 moiety could be found in the A, B, C and D subsites. Significant shifts of the backbone atoms were observed in the region of residues 102 to 120, which composed one side of the wall of the active site cleft. Consequently, the active cleft, with respect to the saccharide binding sites A, B and C, is narrower in both protein molecules. The residues 109 to 111 in site D of MOL1 are moved toward saccharide residue D, whereas those of MOL2 are only slightly shifted. In spite of these facts, the saccharide residues in site MOL1 and MOL2 are moved inside of the cleft. The distribution of water molecules and the hydrogen bond network in site D differ between the structures of MOL1 and MOL2. These structural changes in the active site cleft may be responsible for accommodating the substrate and releasing the products of hydrolysis. These results suggest that the three-dimensional structures of MOL1 and MOL2 remain in intermediate states between a transition state and an enzyme/product complex state.
Organizational Affiliation:
Protein Engineering Research Institute, Osaka, Japan.