Interaction of Kazal-type inhibitor domains with serine proteinases: biochemical and structural studies.
Schlott, B., Wohnert, J., Icke, C., Hartmann, M., Ramachandran, R., Guhrs, K.H., Glusa, E., Flemming, J., Gorlach, M., Grosse, F., Ohlenschlager, O.(2002) J Mol Biology 318: 533-546
- PubMed: 12051857
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-2836(02)00014-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KMA - PubMed Abstract:
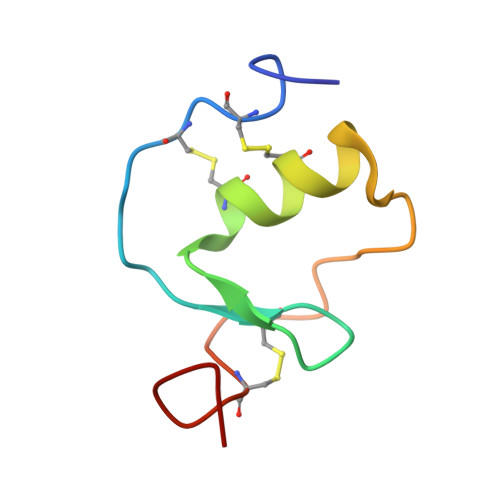
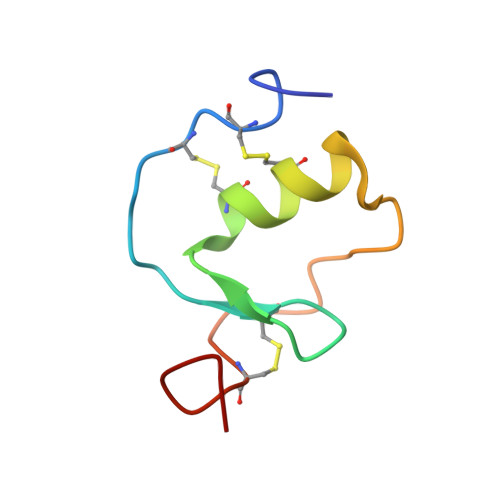
The interaction of domains of the Kazal-type inhibitor protein dipetalin with the serine proteinases thrombin and trypsin is studied. The functional studies of the recombinantly expressed domains (Dip-I+II, Dip-I and Dip-II) allow the dissection of the thrombin inhibitory properties and the identification of Dip-I as a key contributor to thrombin/dipetalin complex stability and its inhibitory potency. Furthermore, Dip-I, but not Dip-II, forms a complex with trypsin resulting in an inhibition of the trypsin activity directed towards protein substrates. The high resolution NMR structure of the Dip-I domain is determined using multi-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Dip-I exhibits the canonical Kazal-type fold with a central alpha-helix and a short two-stranded antiparallel beta-sheet. Molecular regions essential for inhibitor complex formation with thrombin and trypsin are identified. A comparison with molecular complexes of other Kazal-type thrombin and trypsin inhibitors by molecular modeling shows that the N-terminal segment of Dip-I fulfills the structural prerequisites for inhibitory interactions with either proteinase and explains the capacity of this single Kazal-type domain to interact with different proteinases.
Organizational Affiliation:
Institut für Molekulare Biotechnologie e.V., Postfach 100813, D-07708 Jena, Germany.