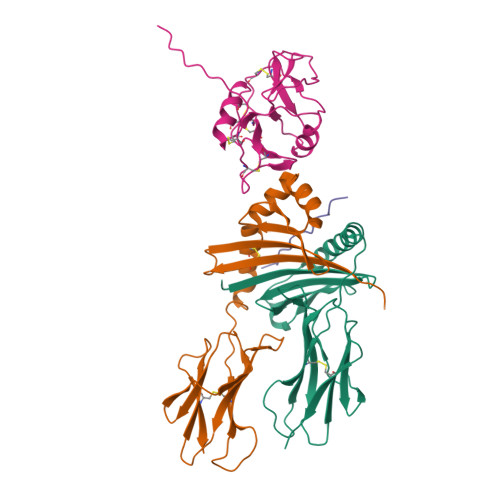
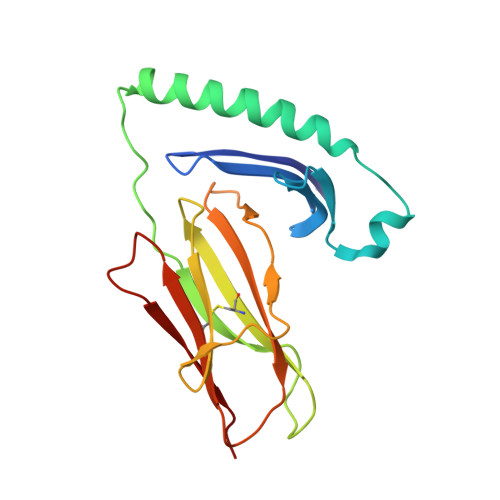
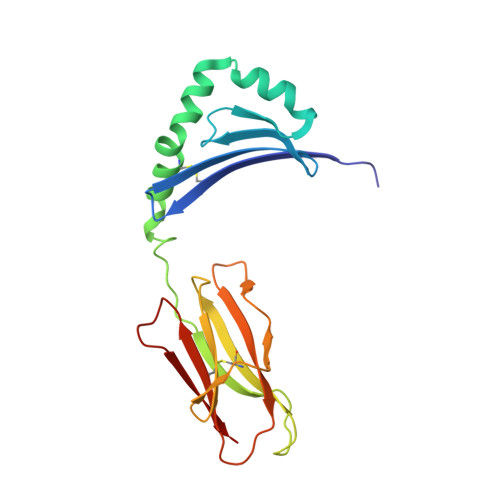
Structure of the Epstein-Barr virus gp42 protein bound to the MHC class II receptor HLA-DR1.
Mullen, M.M., Haan, K.M., Longnecker, R., Jardetzky, T.S.(2002) Mol Cell 9: 375-385
- PubMed: 11864610
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(02)00465-3
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KG0 - PubMed Abstract:
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) causes infectious mononucleosis, establishes long-term latent infections, and is associated with a variety of human tumors. The EBV gp42 glycoprotein binds MHC class II molecules, playing a critical role in infection of B lymphocytes. EBV gp42 belongs to the C-type lectin superfamily, with homology to NK receptors of the immune system. We report the crystal structure of gp42 bound to the human MHC class II molecule HLA-DR1. The gp42 binds HLA-DR1 using a surface site that is distinct from the canonical lectin and NK receptor ligand binding sites. At the canonical ligand binding site, gp42 forms a large hydrophobic groove, which could interact with other ligands necessary for EBV entry, providing a mechanism for coupling MHC recognition and membrane fusion.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Cell Biology, Northwestern University, Evanston, IL 60208, USA.