Crystal Structure of Extracellular Human BAFF, a TNF Family Member that Stimulates B Lymphocytes
Karpusas, M., Cachero, T.G., Qian, F., Boriack-Sjodin, A., Mullen, C., Strauch, K., Hsu, Y.-M., Kalled, S.L.(2002) J Mol Biology 315: 1145-1154
- PubMed: 11827482
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.5296
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1KD7 - PubMed Abstract:
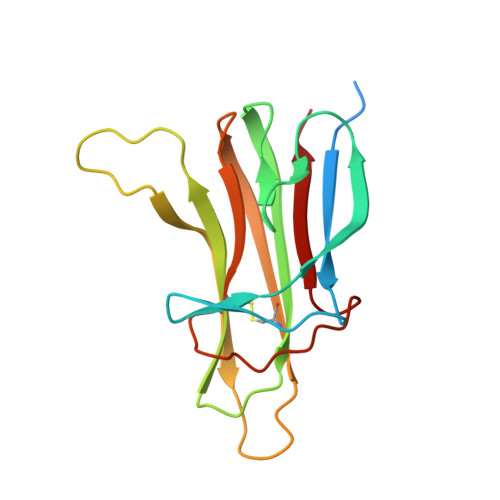
B cell activating factor (BAFF), a ligand belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family, plays a critical role in regulating survival and activation of peripheral B cell populations and has been associated with autoimmune disease. BAFF is known to interact with three receptors, BCMA, TACI and BAFF-R, that have distant similarities with other receptors of the TNF family. We have determined the crystal structure of the TNF-homologous domain of BAFF at 2.8 A resolution. The structure reveals significant differences when compared to other TNF family members, including an unusually long D-E loop that participates in the formation of a deep, concave and negatively charged region in the putative receptor binding site. The BAFF structure was further used to generate a homology model of APRIL, a closely related TNF family ligand that also binds to BCMA and TACI, but not BAFF-R. Analysis of the putative receptor binding sites of BAFF and APRIL suggests that differences in the D-E loop structure and electrostatic surface potentials may be important for determining binding specificities for BCMA, TACI and BAFF-R.
Organizational Affiliation:
Biogen, Inc., 14 Cambridge Center, Cambridge, MA 02142, USA. michael_karpusas@biogen.com