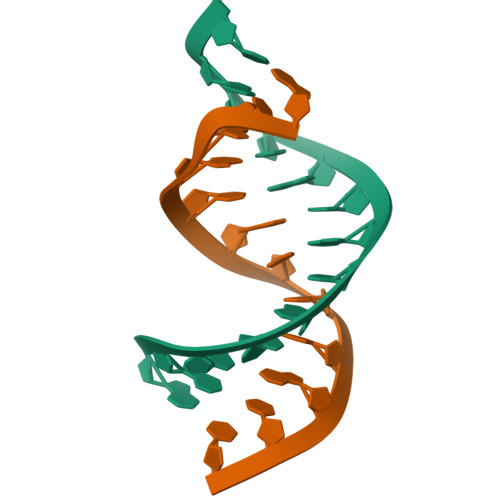
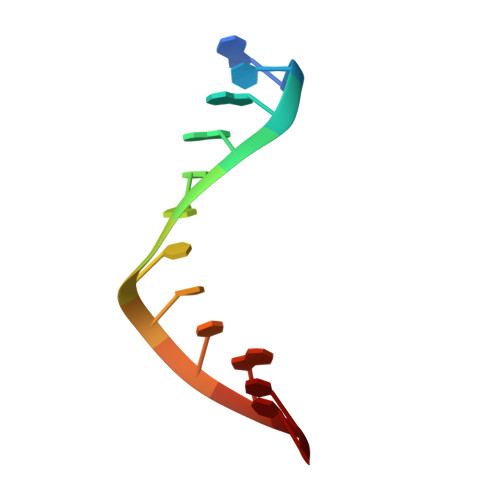
Solution conformation of a bulged adenosine base in an RNA duplex by relaxation matrix refinement.
Thiviyanathan, V., Guliaev, A.B., Leontis, N.B., Gorenstein, D.G.(2000) J Mol Biology 300: 1143-1154
- PubMed: 10903860
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.3931
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1K8S - PubMed Abstract:
Bulges are common structural motifs in RNA secondary structure and are thought to play important roles in RNA-protein and RNA-drug interactions. Adenosine bases are the most commonly occurring unpaired base in double helical RNA secondary structures. The solution conformation and dynamics of a 25-nucleotide RNA duplex containing an unpaired adenosine, r(GGCAGAGUGCCGC): r(GCGGCACCUGCC) have been studied by NMR spectroscopy and MORASS iterative relaxation matrix structural refinement. The results show that the bulged adenosine residue stacks into the RNA duplex with little perturbation around the bulged region. Most of the bases in the RNA duplex adopt C(3)'-endo conformation, exhibiting the N-type sugar pucker as found in the A form helices. The sugars of the bulged residue and the 5' flanking residue to it are found to exhibit C(2)'-endo conformation. None of the residues are in syn conformation.
Organizational Affiliation:
Sealy Center for Structural Biology and Department of Human Biological Chemistry and Genetics, University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston, TX 77555-1157, USA.